Identification of the plasma total cfDNA level before and after chemotherapy as an indicator of the neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in locally advanced breast cancer
- PMID: 32017472
- PMCID: PMC7131846
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2906
Identification of the plasma total cfDNA level before and after chemotherapy as an indicator of the neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in locally advanced breast cancer
Abstract
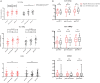
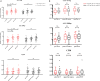
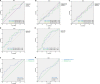
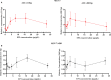
This study aimed to retrospectively evaluate the circulating free DNA (cfDNA) level in patients with locally advanced breast cancer (LABC) having different neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NCT) responses and to investigate whether dynamic changes in cfDNA level could predict the effectiveness of NCT in patients with LABC. Data on 61 patients with LABC were included. NCT responses were evaluated using the response evaluation criteria. Blood samples were collected for cfDNA detection before treatment and after the first and eighth courses of chemotherapy. The Alu 111-bp and 260-bp fragment levels were evaluated by polymerase chain reaction, and the predictive value of the cfDNA level in the NCT response was determined. In vitro, the MCF-7 and MCF-7/ADR cell lines were applied to simulate the phenomenon of drug resistance and explain the underlying mechanism. The Alu 111-bp level increased after the first NCT course (P = .014) and then remained high after NCT in the high-R group (P = .047), but it remained steady in the low-R group during NCT. A similar tendency in the Alu 260-bp level was revealed in different groups. The ∆∆Ct value of Alu 260-bp had good diagnostic efficiency in assessing predictive ability. The area under the curve for the ∆∆Ct1 and ∆∆Ct2 of Alu 260-bp was 0.697 and 0.647, respectively. The cfDNA level was closely related to epirubicin-induced apoptosis and changes in the Ki-67 index in vitro. The elevation of cfDNA after one chemotherapy cycle was mediated by the apoptosis of tumor cells and related to the improved chemotherapy response.
Keywords: apoptosis; biomarkers; breast cancer; neoadjuvant chemotherapy.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7‐34. - PubMed
-
- De Mattos‐Arruda L, Cortes J, Santarpia L, et al. Circulating tumour cells and cell‐free DNA as tools for managing breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10(7):377‐389. - PubMed
-
- Huang ZH, Li LH, Hua D. Quantitative analysis of plasma circulating DNA at diagnosis and during follow‐up of breast cancer patients. Cancer Lett. 2006;243(1):64‐70. - PubMed
-
- Panagopoulou M, Karaglani M, Balgkouranidou I, et al. Circulating cell‐free DNA in breast cancer: size profiling, levels, and methylation patterns lead to prognostic and predictive classifiers. Oncogene. 2019;38(18):3387‐3401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

