Viral reactivations following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients - A single center 11-year analysis
- PMID: 32017805
- PMCID: PMC6999888
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228451
Viral reactivations following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in pediatric patients - A single center 11-year analysis
Abstract
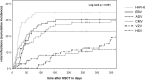
Viral reactivation occurs frequently in the context of immunodeficiency and immunosuppression after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) and can cause severe complications. The aim of this single-center retrospective analysis was to characterize viral infections in the first year after HSCT, to investigate risk factors and to study the impact of viral infections on transplantation outcome. This will facilitate the identification of at-risk patients and the development of new preventive strategies. 107 pediatric allo-HSCT from January 2005 through December 2015 were analyzed for infections with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), adenovirus (ADV), herpes simplex virus (HSV) and varicella zoster virus (VZV). Viral infections were detected after 68.2% of transplantations. The viruses most commonly encountered were HHV-6 (36/107) and EBV (30/107). Severe viral disease was rare (7/107) and none of the patients died as result of viral reactivation. Important risk factors for viral infections were higher age at HSCT, donor type and occurrence of acute graft-versus-host disease (aGvHD). Especially for EBV, transplant from an unrelated donor and in-vivo T-cell depletion (TCD) had a significant effect on infection rates, whereas for CMV the strongest effect was seen by donor and recipient serostatus with recipient seropositivity most predictive for reactivation. The occurrence of severe aGvHD was associated with EBV and ADV infections. For HSV, the recipient serostatus was identified as prognostic factor for HSV infections, while we found higher age at time of HSCT as risk factor for VZV infections. The overall survival of patients with or without viral infections did not differ significantly. Interestingly, when looking at the 85 patients in our cohort who had received an HSCT for a malignant disease, a tendency towards lower relapse rates was seen in patients affected by viral infections (HR 0.51, 95% CI 0.25 - 1.06, p = 0.072). Viral reactivations are common after pediatric allo-HSCT, though severe complications were rare in our collective. Determining risk factors for viral reactivations may help to identify patients in need of intensified monitoring and to individualize preventive strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Olkinuora HA, Taskinen MH, Saarinen-Pihkala UM, Vettenranta KK. Multiple viral infections post-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation are linked to the appearance of chronic GVHD among pediatric recipients of allogeneic grafts. Pediatr Transplant. 2010;14(2):242–8. 10.1111/j.1399-3046.2009.01226.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Srinivasan A, Wang C, Srivastava DK, Burnette K, Shenep JL, Leung W, et al. Timeline, epidemiology, and risk factors for bacterial, fungal, and viral infections in children and adolescents after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(1):94–101. 10.1016/j.bbmt.2012.08.012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vermont CL, Jol-van der Zijde EC, Hissink Muller P, Ball LM, Bredius RG, Vossen AC, et al. Varicella zoster reactivation after hematopoietic stem cell transplant in children is strongly correlated with leukemia treatment and suppression of host T-lymphocyte immunity. Transpl Infect Dis. 2014;16(2):188–94. 10.1111/tid.12180 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

