The peroxisomal fatty acid transporter ABCD1/PMP-4 is required in the C. elegans hypodermis for axonal maintenance: A worm model for adrenoleukodystrophy
- PMID: 32017990
- PMCID: PMC7611262
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.01.177
The peroxisomal fatty acid transporter ABCD1/PMP-4 is required in the C. elegans hypodermis for axonal maintenance: A worm model for adrenoleukodystrophy
Abstract
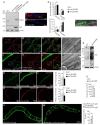
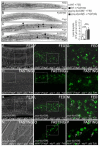
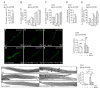
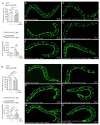
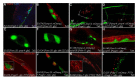
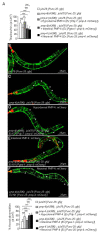
Adrenoleukodystrophy is a neurometabolic disorder caused by a defective peroxisomal ABCD1 transporter of very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs). Its pathogenesis is incompletely understood. Here we characterize a nematode model of X-ALD with loss of the pmp-4 gene, the worm orthologue of ABCD1. These mutants recapitulate the hallmarks of X-ALD: i) VLCFAs accumulation and impaired mitochondrial redox homeostasis and ii) axonal damage coupled to locomotor dysfunction. Furthermore, we identify a novel role for PMP-4 in modulating lipid droplet dynamics. Importantly, we show that the mitochondria targeted antioxidant MitoQ normalizes lipid droplets size, and prevents axonal degeneration and locomotor disability, highlighting its therapeutic potential. Moreover, PMP-4 acting solely in the hypodermis rescues axonal and locomotion abnormalities, suggesting a myelin-like role for the hypodermis in providing essential peroxisomal functions for the nematode nervous system.
Keywords: Axonal degeneration; Hypodermis; Lipid droplets; Mitochondria redox imbalance; Peroxisomes; X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Waterham HR, Ferdinandusse S, Wanders RJ. Human disorders of peroxisome metabolism and biogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863(5):922–33. - PubMed
-
- Moser AB, Fatemi A. Newborn Screening and Emerging Therapies for X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy. JAMA Neurol. 2018:e - PubMed
-
- van Roermund CW, Visser WF, Ijlst L, van Cruchten A, Boek M, Kulik W, Waterham HR, Wanders RJ. The human peroxisomal ABC half transporter ALDP functions as a homodimer and accepts acyl-CoA esters. Faseb J. 2008;22(12):4201–8. - PubMed
-
- Engelen M, Kemp S, Poll-The BT. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: pathogenesis and treatment. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2014;14(10):486. - PubMed

