New Approaches to SCLC Therapy: From the Laboratory to the Clinic
- PMID: 32018053
- PMCID: PMC7263769
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtho.2020.01.016
New Approaches to SCLC Therapy: From the Laboratory to the Clinic
Abstract
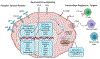
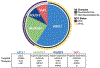
The outcomes of patients with SCLC have not yet been substantially impacted by the revolution in precision oncology, primarily owing to a paucity of genetic alterations in actionable driver oncogenes. Nevertheless, systemic therapies that include immunotherapy are beginning to show promise in the clinic. Although, these results are encouraging, many patients do not respond to, or rapidly recur after, current regimens, necessitating alternative or complementary therapeutic strategies. In this review, we discuss ongoing investigations into the pathobiology of this recalcitrant cancer and the therapeutic vulnerabilities that are exposed by the disease state. Included within this discussion, is a snapshot of the current biomarker and clinical trial landscapes for SCLC. Finally, we identify key knowledge gaps that should be addressed to advance the field in pursuit of reduced SCLC mortality. This review largely summarizes work presented at the Third Biennial International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer SCLC Meeting.
Keywords: ASCL1; Gene mutations; Neuroendocrine; SCLC; Therapy.
Copyright © 2020 International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Howlader N, et al. , SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2016, National Cancer Institute; 2019.
-
- Hanahan D and Weinberg RA, Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell, 2011. 144(5): p. 646–74. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D and Weinberg RA, The hallmarks of cancer. Cell, 2000. 100(1): p. 57–70. - PubMed
-
- Horn L, et al. , First-Line Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med, 2018. 379(23): p. 2220–2229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 CA213273/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA231851/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA213359/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA231844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA207295/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA213448/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 20465/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U54 CA217450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA213338/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA181449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA213274/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA226353/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA216504/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 19278/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R35 CA231997/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA242919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA222657/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 29420/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- K99 CA201618/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 29569/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

