Baicalin alleviates benign prostate hyperplasia through androgen-dependent apoptosis
- PMID: 32018227
- PMCID: PMC7041748
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.102731
Baicalin alleviates benign prostate hyperplasia through androgen-dependent apoptosis
Abstract
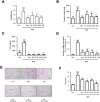
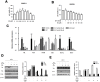
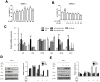
BPH is a disease prevalent among elderly men that is characterized by abnormal proliferation of prostatic epithelial and stromal tissues. No effective treatment exists for BPH owing to lack of a clear understanding of its molecular etiology. Although several studies have reported therapeutic effects of baicalin against numerous diseases, including prostate cancer, its beneficial effects on BPH have not yet been explored. The present study investigated the therapeutic effects of baicalin on the development of BPH and its mechanism of action. We established a testosterone-treated BPH animal model and DHT-stimulated prostate cell lines, including RWPE-1 and WPMY-1. Administration of baicalin ameliorated the pathological prostate enlargement, suppressed the production of DHT, and inhibited the activity of 5α- reductase Type II in the animal model. BC exerted these effects via its anti-proliferative effects by restoring the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, activating caspase-3 and caspase-8, and inducing the phosphorylation of AMPK. In vitro studies using DHT-stimulated prostate cells demonstrated an up-regulation of BPH-related and proliferation markers, whereas baicalin clearly reduced the overexpression of AR, PSA, PCNA, and Bcl-2. These results suggested that baicalin could suppress androgen-dependent development of BPH both in vivo and in vitro by inducing apoptosis.
Keywords: androgen; apoptosis; baicalin; benign prostatic hyperplasia; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

