Effects of 2-Week Exercise Training in Hypobaric Hypoxic Conditions on Exercise Performance and Immune Function in Korean National Cycling Athletes with Disabilities: A Case Report
- PMID: 32019079
- PMCID: PMC7037344
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17030861
Effects of 2-Week Exercise Training in Hypobaric Hypoxic Conditions on Exercise Performance and Immune Function in Korean National Cycling Athletes with Disabilities: A Case Report
Abstract
We aimed to evaluate the effects of a 2-week exercise training program in hypobaric hypoxic conditions on exercise performance and immune function in Korean national cycling athletes with disabilities. Six Korean national cycling athletes with disabilities participated in exercise training consisting of continuous aerobic exercise and anaerobic interval exercise in hypobaric hypoxic conditions. The exercise training frequency was 60 min (5 days per week for 2 weeks). Before and after the exercise training, exercise performance and immune function were measured in all athletes. Regarding the exercise performance parameters, the 3-km time trial significantly decreased and blood lactate levels after the 3-km time trial test significantly increased by exercise training in hypobaric hypoxic conditions. Regarding the oxygen-transporting capacity, significant differences were not observed. Regarding immune function, the number of leukocytes and natural killer cells significantly decreased and that of eosinophils, B cells, and T cells significantly increased. These results indicated that our 2-week hypoxic training showed the potential to improve exercise performance in Korean national disabled athletes. However, the effects of our hypoxic training method on immune function remained unclear.
Keywords: athletes with disability; exercise performance; hypobaric hypoxic training; immune function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
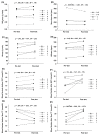
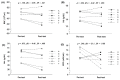

References
-
- Girard O., Amann M., Aughey R., Billaut F., Bishop D.J., Bourdon P., Buchheit M., Chapman R., D’Hooghe M., Garvican-Lewis L.A., et al. Position statement—Altitude training for improving team-sport players’ performance: Current knowledge and unresolved issues. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013;47(Suppl. 1):i8–i16. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2013-093109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

