Host Transcription Factors in Hepatitis B Virus RNA Synthesis
- PMID: 32019103
- PMCID: PMC7077322
- DOI: 10.3390/v12020160
Host Transcription Factors in Hepatitis B Virus RNA Synthesis
Abstract
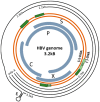
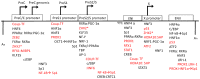
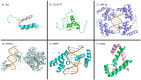
The hepatitis B virus (HBV) chronically infects over 250 million people worldwide and is one of the leading causes of liver cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma. HBV persistence is due in part to the highly stable HBV minichromosome or HBV covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) that resides in the nucleus. As HBV replication requires the help of host transcription factors to replicate, focusing on host protein-HBV genome interactions may reveal insights into new drug targets against cccDNA. The structural details on such complexes, however, remain poorly defined. In this review, the current literature regarding host transcription factors' interactions with HBV cccDNA is discussed.
Keywords: covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA); hepatitis B virus (HBV); host–viral interactions; transcription factors; viral replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA and Minichromosome Formation and HBV Gene Transcription.Viruses. 2024 Apr 15;16(4):609. doi: 10.3390/v16040609. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38675950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revisiting Hepatitis B Virus: Challenges of Curative Therapies.J Virol. 2019 Sep 30;93(20):e01032-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01032-19. Print 2019 Oct 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31375584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HBVcircle: A novel tool to investigate hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA.J Hepatol. 2017 Jun;66(6):1149-1157. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.02.004. Epub 2017 Feb 14. J Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28213165
-
PRMT5 restricts hepatitis B virus replication through epigenetic repression of covalently closed circular DNA transcription and interference with pregenomic RNA encapsidation.Hepatology. 2017 Aug;66(2):398-415. doi: 10.1002/hep.29133. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Hepatology. 2017. PMID: 28236308
-
Early Steps of Hepatitis B Life Cycle: From Capsid Nuclear Import to cccDNA Formation.Viruses. 2021 Apr 26;13(5):757. doi: 10.3390/v13050757. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33925977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Classifying hepatitis B therapies with insights from covalently closed circular DNA dynamics.Virol Sin. 2024 Feb;39(1):9-23. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2023.12.005. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Virol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38110037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psoralen inhibits hepatitis B viral replication by down-regulating the host transcriptional machinery of viral promoters.Virol Sin. 2022 Apr;37(2):256-265. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.01.027. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Virol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35305922 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of viral hepatitis induced hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Oct 14;26(38):5759-5783. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i38.5759. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 33132633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term HBV infection of engineered cultures of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes.Hepatol Commun. 2024 Jul 31;8(8):e0506. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000506. eCollection 2024 Aug 1. Hepatol Commun. 2024. PMID: 39082962 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian control of hepatitis B virus replication.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 12;12(1):1658. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21821-0. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33712578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . Global Hepatitis Report 2017. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017. p. 7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

