Differential Effects of 2-Hydroxypropyl-Cyclodextrins on Lipid Accumulation in Npc1-Null Cells
- PMID: 32019132
- PMCID: PMC7038050
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21030898
Differential Effects of 2-Hydroxypropyl-Cyclodextrins on Lipid Accumulation in Npc1-Null Cells
Abstract
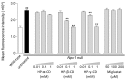
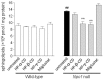
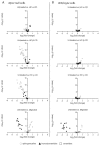
Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by abnormal accumulation of free cholesterol and sphingolipids in lysosomes. The iminosugar miglustat, which inhibits hexosylceramide synthesis, is used for NPC treatment, and 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HP-β-CD), a cyclic oligosaccharide derivative, is being developed to treat NPC. Moreover, therapeutic potential of 2-hydroxypropyl-γ-cyclodextrin (HP-γ-CD) was shown in NPC models, although its mechanism of action remains unclear. Here, we investigated the effects of HP-β-CD, HP-γ-CD, and their homolog 2-hydroxypropyl-α-cyclodextrin (HP-α-CD) on lipid accumulation in Npc1-null Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells compared with those of miglustat. HP-β-CD and HP-γ-CD, unlike HP-α-CD, reduced intracellular free cholesterol levels and normalized the lysosome changes in Npc1-null cells but not in wild-type CHO cells. In contrast, miglustat did not normalize intracellular free cholesterol accumulation or lysosome changes in Npc1-null cells. However, miglustat decreased the levels of hexosylceramide and tended to increase those of sphingomyelins in line with its action as a glucosylceramide synthase inhibitor in both Npc1-null and wild-type CHO cells. Interestingly, HP-β-CD and HP-γ-CD, unlike HP-α-CD, reduced sphingomyelins in Npc1-null, but not wild-type, cells. In conclusion, HP-β-CD and HP-γ-CD reduce the accumulation of sphingolipids, mainly sphingomyelins, and free cholesterol as well as lysosome changes in Npc1-null, but not in wild-type, CHO cells.
Keywords: 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin; 2-hydroxypropyl-γ-cyclodextrin; Niemann–Pick disease type C; cholesterol; cyclodextrin; lysosome; miglustat; sphingolipid; sphingomyelin.
Conflict of interest statement
A.H. and T.K. are employees of Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vitro evaluation of 2-hydroxyalkylated β-cyclodextrins as potential therapeutic agents for Niemann-Pick Type C disease.Mol Genet Metab. 2016 Jul;118(3):214-219. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.04.014. Epub 2016 Apr 30. Mol Genet Metab. 2016. PMID: 27184436
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of 6-O-α-Maltosyl-β-Cyclodextrin as a Potential Therapeutic Agent Against Niemann-Pick Disease Type C.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 6;20(5):1152. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051152. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30845767 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxypropyl-beta and -gamma cyclodextrins rescue cholesterol accumulation in Niemann-Pick C1 mutant cell via lysosome-associated membrane protein 1.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Oct 3;9(10):1019. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1056-1. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30282967 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclodextrins applied to the treatment of lysosomal storage disorders.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Dec;191:114617. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114617. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 36356931 Review.
-
Collaborative development of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin for the treatment of Niemann-Pick type C1 disease.Curr Top Med Chem. 2014;14(3):330-9. doi: 10.2174/1568026613666131127160118. Curr Top Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24283970 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Searching, Structural Determination, and Diagnostic Performance Evaluation of Biomarker Molecules for Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Using Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry.Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2022;11(1):A0111. doi: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0111. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Mass Spectrom (Tokyo). 2022. PMID: 36713801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inability of α-cyclodextrins to accommodate cholesterol potentially underlies their lack of efficacy and ototoxicity in Niemann-Pick disease type C treatment.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 22;15(1):30857. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15599-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40847051 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclodextrins: Only Pharmaceutical Excipients or Full-Fledged Drug Candidates?Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 22;14(12):2559. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122559. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid-mediated motor-adaptor sequestration impairs axonal lysosome delivery leading to autophagic stress and dystrophy in Niemann-Pick type C.Dev Cell. 2021 May 17;56(10):1452-1468.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.03.032. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Dev Cell. 2021. PMID: 33878344 Free PMC article.
-
Niemann-Pick Disease Type C (NPDC) by Mutation of NPC1 and NPC2: Aberrant Lysosomal Cholesterol Trafficking and Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 21;12(12):2021. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122021. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136141 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

