Deep Hypersaline Anoxic Basins as Untapped Reservoir of Polyextremophilic Prokaryotes of Biotechnological Interest
- PMID: 32019162
- PMCID: PMC7074082
- DOI: 10.3390/md18020091
Deep Hypersaline Anoxic Basins as Untapped Reservoir of Polyextremophilic Prokaryotes of Biotechnological Interest
Abstract
Deep-sea hypersaline anoxic basins (DHABs) are considered to be among the most extreme ecosystems on our planet, allowing only the life of polyextremophilic organisms. DHABs' prokaryotes exhibit extraordinary metabolic capabilities, representing a hot topic for microbiologists and biotechnologists. These are a source of enzymes and new secondary metabolites with valuable applications in different biotechnological fields. Here, we review the current knowledge on prokaryotic diversity in DHABs, highlighting the biotechnological applications of identified taxa and isolated species. The discovery of new species and molecules from these ecosystems is expanding our understanding of life limits and is expected to have a strong impact on biotechnological applications.
Keywords: blue biotechnologies; deep hypersaline anoxic basins; extremozymes; limits of life; marine prokaryotes; microbial diversity; polyextremophiles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
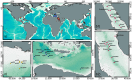

References
-
- Herring P.J. The biology of the deep ocean. Oxford University Press; New York, NY, USA: 2001. pp. 1–25.
-
- Bartlett D.H. Microbial Life in the Trenches. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 2009;43:128–131. doi: 10.4031/MTSJ.43.5.5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

