Alternative Structures of α-Synuclein
- PMID: 32019169
- PMCID: PMC7038196
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25030600
Alternative Structures of α-Synuclein
Abstract
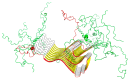
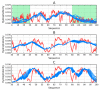
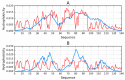
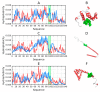
The object of our analysis is the structure of alpha-synuclein (ASyn), which, under in vivo conditions, associates with presynaptic vesicles. Misfolding of ASyn is known to be implicated in Parkinson's disease. The availability of structural information for both the micelle-bound and amyloid form of ASyn enables us to speculate on the specific mechanism of amyloid transformation. This analysis is all the more interesting given the fact that-Unlike in Aβ(1-42) amyloids-only the central fragment (30-100) of ASyn has a fibrillar structure, whereas, its N- and C-terminal fragments (1-30 and 100-140, respectively) are described as random coils. Our work addresses the following question: Can the ASyn chain-as well as the aforementioned individual fragments-adopt globular conformations? In order to provide an answer, we subjected the corresponding sequences to simulations carried out using Robetta and I-Tasser, both of which are regarded as accurate protein structure predictors. In addition, we also applied the fuzzy oil drop (FOD) model, which, in addition to optimizing the protein's internal free energy, acknowledges the presence of an external force field contributed by the aqueous solvent. This field directs hydrophobic residues to congregate near the center of the protein body while exposing hydrophilic residues on its surface. Comparative analysis of the obtained models suggests that fragments which do not participate in forming the amyloid fibril (i.e., 1-30 and 100-140) can indeed attain globular conformations. We also explain the influence of mutations observed in vivo upon the susceptibility of ASyn to undergo amyloid transformation. In particular, the 30-100 fragment (which adopts a fibrillar structure in PDB) is not predicted to produce a centralized hydrophobic core by any of the applied toolkits (Robetta, I-Tasser, and FOD). This means that in order to minimize the entropically disadvantageous contact between hydrophobic residues and the polar solvent, ASyn adopts the form of a ribbonlike micelle (rather than a spherical one). In other words, the ribbonlike micelle represents a synergy between the conformational preferences of the protein chain and the influence of its environment.
Keywords: A-synuclein; amyloid; fibril; hydrophobicity; misfolding; protein folding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Structural Specificity of Polymorphic Forms of α-Synuclein Amyloid.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 29;11(5):1324. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051324. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37238996 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analysis of the Aβ(11-42) amyloid fibril based on hydrophobicity distribution.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2019 Jul;33(7):665-675. doi: 10.1007/s10822-019-00209-9. Epub 2019 Jul 10. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2019. PMID: 31292794 Free PMC article.
-
The Amyloid as a Ribbon-Like Micelle in Contrast to Spherical Micelles Represented by Globular Proteins.Molecules. 2019 Dec 3;24(23):4395. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234395. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31816829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrinsic Conformational Preferences and Interactions in α-Synuclein Fibrils: Insights from Molecular Dynamics Simulations.J Chem Theory Comput. 2018 Jun 12;14(6):3298-3310. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.8b00183. Epub 2018 May 10. J Chem Theory Comput. 2018. PMID: 29715424
-
The Cellular Environment Affects Monomeric α-Synuclein Structure.Trends Biochem Sci. 2019 May;44(5):453-466. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2018.11.005. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Trends Biochem Sci. 2019. PMID: 30527975 Review.
Cited by
-
The structural heterogeneity of α-synuclein is governed by several distinct subpopulations with interconversion times slower than milliseconds.Structure. 2021 Sep 2;29(9):1048-1064.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2021.05.002. Epub 2021 May 19. Structure. 2021. PMID: 34015255 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Specificity of Polymorphic Forms of α-Synuclein Amyloid.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 29;11(5):1324. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051324. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37238996 Free PMC article.
-
The Structure of Amyloid Versus the Structure of Globular Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 30;21(13):4683. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134683. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32630137 Free PMC article.
-
Potential value of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein in the identification of postoperative delirium undergoing knee/hip arthroplasty: The perioperative neurocognitive disorder and biomarker lifestyle study.Front Neurosci. 2022 Oct 24;16:935869. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.935869. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36353596 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid Oligomers: A Joint Experimental/Computational Perspective on Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, Type II Diabetes, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Chem Rev. 2021 Feb 24;121(4):2545-2647. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01122. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Chem Rev. 2021. PMID: 33543942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

