High-Efficiency Small Sample Microparticle Fractionation on a Femtosecond Laser-Machined Microfluidic Disc
- PMID: 32019235
- PMCID: PMC7074639
- DOI: 10.3390/mi11020151
High-Efficiency Small Sample Microparticle Fractionation on a Femtosecond Laser-Machined Microfluidic Disc
Abstract
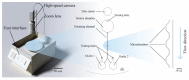
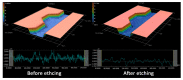
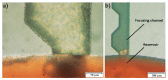
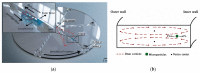
The fabrication and testing of microfluidic spinning compact discs with embedded trapezoidal microchambers for the purpose of inertial microparticle focusing is reported in this article. Microparticle focusing channels require small features that cannot be easily fabricated in acrylic sheets and are complicated to realize in glass by traditional lithography techniques; therefore, the fabrication of microfluidic discs with femtosecond laser ablation is reported for the first time in this paper. It could be demonstrated that high-efficiency inertial focusing of 5 and 10 µm particles is achieved in a channel with trapezoidal microchambers regardless of the direction of disc rotation, which correlates to the dominance of inertial forces over Coriolis forces. To achieve the highest throughput possible, the suspension concentration was increased from 0.001% (w/v) to 0.005% (w/v). The focusing efficiency was 98.7% for the 10 µm particles and 93.75% for the 5 µm particles.
Keywords: femtosecond laser; microfluidic disc; microfluidics; microparticle separation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Krull R., Wucherpfennig T., Esfandabadi M.E., Walisko R., Melzer G., Hempel D.C., Kampen I., Kwade A., Wittmann C. Characterization and control of fungal morphology for improved production performance in biotechnology. J. Biotechnol. 2013;163:112–123. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.06.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khoo B.L., Warkiani M.E., Tan D.S.-W., Bhagat A.A.S., Irwin D., Lau D.P., Lim A.S.T., Lim K.H., Krisna S.S., Lim W.-T., et al. Clinical Validation of an Ultra High-Throughput Spiral Microfluidics for the Detection and Enrichment of Viable Circulating Tumor Cells. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e99409. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099409. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al-Faqheri W., Thio T.H.G., Qasaimeh M.A., Dietzel A., Madou M., Al-Halhouli A. Particle/cell separation on microfluidic platforms based on centrifugation effect: a review. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2017;21:1–23. doi: 10.1007/s10404-017-1933-4. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

