Leucine Improved Growth Performance, Muscle Growth, and Muscle Protein Deposition Through AKT/TOR and AKT/FOXO3a Signaling Pathways in Hybrid Catfish Pelteobagrus v achelli × Leiocassis longirostris
- PMID: 32019276
- PMCID: PMC7072317
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9020327
Leucine Improved Growth Performance, Muscle Growth, and Muscle Protein Deposition Through AKT/TOR and AKT/FOXO3a Signaling Pathways in Hybrid Catfish Pelteobagrus v achelli × Leiocassis longirostris
Abstract
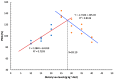
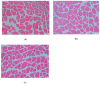
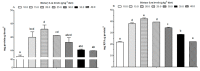
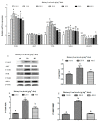
(1) Background: l-leucine (Leu) plays a positive role in regulating protein turnover in skeletal muscle in mammal. However, the molecular mechanism for the effects of Leu on muscle growth and protein deposition is not clearly demonstrated in fish. This study investigated the effects of dietary Leu on growth performance and muscle growth, protein synthesis, and degradation-related signaling pathways of hybrid catfish (Pelteobagrus vachelli♀ × Leiocassis longirostris♂). (2) Methods: A total of 630 hybrid catfish (23.19 ± 0.20 g) were fed 6 different experimental diets containing graded levels of Leu at 10.0 (control), 15.0, 20.0, 25.0, 30.0, 35.0, and 40.0 g Leu kg-1 for 8 weeks. (3) Results: Results showed that dietary Leu increased percent weight gain (PWG), specific growth rate (SGR), FI (feed intake), feed efficiency (FE), protein efficiency ratio (PER), muscle fibers diameter, and muscle fibers density; up-regulated insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR), proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), myogenic regulation factors (MyoD, Myf5, MyoG, and Mrf4), and MyHC mRNA levels; increased muscle protein synthesis via regulating the AKT/TOR signaling pathway; and attenuated protein degradation via regulating the AKT/FOXO3a signaling pathway. (4) Conclusions: These results suggest that Leu has potential role to improve muscle growth and protein deposition in fish, which might be due to the regulation of IGF mRNA expression, muscle growth related gene, and protein synthesis and degradation-related signaling pathways. Based on the broken-line model, the Leu requirement of hybrid catfish (23.19-54.55 g) for PWG was estimated to be 28.10 g kg-1 of the diet (73.04 g kg-1 of dietary protein). These results will improve our understanding of the mechanisms responsible for muscle growth and protein deposition effects of Leu in fish.
Keywords: hybrid bagrid catfish; leucine; muscle growth; protein degradation; protein synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of dietary threonine on growth performance and muscle growth, protein synthesis and antioxidant-related signalling pathways of hybrid catfish Pelteobagrus vachelli♀ × Leiocassis longirostris♂.Br J Nutr. 2020 Jan 28;123(2):121-134. doi: 10.1017/S0007114519002599. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Br J Nutr. 2020. PMID: 31637992
-
Dietary isoleucine improved flesh quality, muscle antioxidant capacity, and muscle growth associated with AKT/TOR/S6K1 and AKT/FOXO3a signaling in hybrid bagrid catfish (Pelteobagrus vachelli♀ × Leiocassis longirostris♂).J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2021 Apr 19;12(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s40104-021-00572-4. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33866964 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary tryptophan on muscle growth, protein synthesis and antioxidant capacity in hybrid catfish Pelteobagrus vachelli♀ × Leiocassis longirostris♂.Br J Nutr. 2022 Jun 28;127(12):1761-1773. doi: 10.1017/S0007114521002828. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Br J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34321122
-
Regulation of muscle hypertrophy: Involvement of the Akt-independent pathway and satellite cells in muscle hypertrophy.Exp Cell Res. 2021 Dec 15;409(2):112907. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112907. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Exp Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 34793776 Review.
-
IL-6 and IGF-1 Signaling Within and Between Muscle and Bone: How Important is the mTOR Pathway for Bone Metabolism?Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2015 Jun;13(3):131-9. doi: 10.1007/s11914-015-0264-1. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2015. PMID: 25712618 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary Supplementation With Hydroxyproline Enhances Growth Performance, Collagen Synthesis and Muscle Quality of Carassius auratus Triploid.Front Physiol. 2022 Jun 1;13:913800. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.913800. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35721560 Free PMC article.
-
Determining the Potential Roles of Branched-Chain Amino Acids in the Regulation of Muscle Growth in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Based on Transcriptome and MicroRNA Sequencing.Aquac Nutr. 2023 Jun 3;2023:7965735. doi: 10.1155/2023/7965735. eCollection 2023. Aquac Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37303609 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary supplementation with glutamate improves the flesh quality of gibel carp (Carassius gibelio) by altering muscle texture characteristics and increasing the deposition of flavour substances.J Nutr Sci. 2025 Jul 14;14:e47. doi: 10.1017/jns.2025.10009. eCollection 2025. J Nutr Sci. 2025. PMID: 40692551 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary leucine requirement of fingerling Channa punctatus (Bloch) based on growth, feed conversion and leucine retention efficiency, hematological parameters, antioxidant and intestinal enzyme activities.Amino Acids. 2023 Apr;55(4):451-468. doi: 10.1007/s00726-023-03240-1. Epub 2023 Jan 22. Amino Acids. 2023. PMID: 36682022
-
Aflatoxin B1 decreased flesh flavor and inhibited muscle development in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella).Anim Nutr. 2024 Mar 29;18:27-38. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.03.012. eCollection 2024 Sep. Anim Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39026602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vélez E.J., Lutfi E., Azizi S., Perelló M., Salmerón C., Riera-Codina M., Ibarz A., Fernández-Borràs J., Blasco J., Capilla E., et al. Understanding fish muscle growth regulation to optimize aquaculture production. Aquaculture. 2017;467:28–40. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.07.004. - DOI
-
- Periago M.J., Ayala M.D., López-Albors O., Abdel I., Martínez C., García-Alcázar A., Ros G., Gil F. Muscle cellularity and flesh quality of wild and farmed sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L. Aquaculture. 2005;249:175–188. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.02.047. - DOI
-
- Rowlerson A., Veggetti A. In: 5-Cellular mechanisms of post-embryonic muscle growth in aquaculture species. Fish Physiology. Johnston I.A., editor. Volume 18. Academic Press; San Diego, CA, USA: 2001. pp. 103–140.
-
- Johnston I.A., Lee H., Macqueen D.J., Paranthaman K., Kawashima C., Anwar A., Kinghorn J.R., Dalmay T. Embryonic temperature affects muscle fibre recruitment in adult zebrafish: Genome-wide changes in gene and microRNA expression associated with the transition from hyperplastic to hypertrophic growth phenotypes. J. Exp. Biol. 2009;212:1781–1793. doi: 10.1242/jeb.029918. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

