HIV treatment in Guinea-Bissau: room for improvement and time for new treatment options
- PMID: 32019545
- PMCID: PMC6998355
- DOI: 10.1186/s12981-020-0259-6
HIV treatment in Guinea-Bissau: room for improvement and time for new treatment options
Abstract
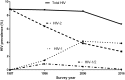
Despite advances in the treatment quality of HIV throughout the world, several countries are still facing numerous obstacles in delivering HIV treatment at a sufficiently high quality, putting patients' lives in jeopardy. The aim of this status article is to give an overview of HIV treatment outcomes in the West African country, Guinea-Bissau, and to assess how newer treatment strategies such as long-acting injectable drugs or an HIV cure may limit or stop the HIV epidemic in this politically unstable and low-resource setting. Several HIV cohorts in Guinea-Bissau have been established and are used as platforms for epidemiological, virological, immunological and clinical studies often with a special focus on HIV-2, which is prevalent in the country. The Bandim Health Project, a demographic surveillance site, has performed epidemiological HIV surveys since 1987 among an urban population in the capital Bissau. The Police cohort, an occupational cohort of police officers, has enabled analyses of persons seroconverting with estimated times of seroconversion among HIV-1 and HIV-2-infected individuals, allowing incidence measurements while the Bissau HIV Cohort and a newer Nationwide HIV Cohort have provided clinical data on large numbers of HIV-infected patients. The HIV cohorts in Guinea-Bissau are unique platforms for research and represent real life in many African countries. Poor adherence, lack of HIV viral load measurements, inadequate laboratory facilities, high rates of loss to follow-up, mortality, treatment failure and resistance development, are just some of the challenges faced putting the goal of "90-90-90″ for Guinea-Bissau well out of reach by 2020. Maintaining undetectable viral loads on treatment as a prerequisite of a cure strategy seems not possible at the moment. Thinking beyond one-pill-once-a-day, long-acting antiretroviral treatment options such as injectable drugs or implants may be a better treatment option in settings like Guinea-Bissau and may even pave the way for an HIV cure. If the delivery of antiretroviral treatment in sub-Saharan Africa in a sustainable way for the future should be improved by focusing on existing treatment options or through focusing on new treatment options remains to be determined.
Keywords: Antiretroviral treatment; Dual infection; Guinea-Bissau; HIV-1; HIV-2; West Africa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical