Ongoing mumps outbreak among adolescents and young adults, Ireland, August 2018 to January 2020
- PMID: 32019666
- PMCID: PMC7001241
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.4.2000047
Ongoing mumps outbreak among adolescents and young adults, Ireland, August 2018 to January 2020
Abstract
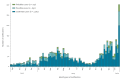
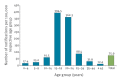
Between 18 August 2018 and 24 January 2020, 3,736 mumps cases were notified in Ireland. The highest numbers of notifications were observed in the age group 15-24 years. Vaccination status was reported for 32% (n = 1,199) of cases: 72% of these had received two doses of measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine. Vaccination uptake after free MMR vaccination targeting colleges and universities since early 2019 was low. Therefore, a national media campaign began in January 2020.
Keywords: Ireland; MMR; mumps; outbreak; young adults.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Government of Ireland. Infectious Diseases (Amendment) Regulations, 1988. Statutory Instrument S.I. No. 288 of 1988. Dublin: Office of the Attorney General; 1988. Available from: http://www.irishstatutebook.ie/1988/en/si/0288.html
-
- Health Service Executive (HSE) Health Protection Surveillance Centre (HPSC). Mumps (Mumps virus). Dublin: HPSC; 2019. Available from: https://www.hpsc.ie/a-z/vaccinepreventable/mumps/casedefinition/
-
- Health Service Executive (HSE) Health Protection Surveillance Centre (HPSC). Mumps in Ireland, 2017. Dublin: HPSC; 2018. Available from: https://www.hpsc.ie/a-z/vaccinepreventable/mumps/publications/annualrepo...
-
- Health Service Executive (HSE) Health Protection Surveillance Centre (HPSC). Summary Immunisation Uptake Statistics Data up to Q2 2019. Dublin: HPSC; 2019. Available from: https://www.hpsc.ie/a-z/vaccinepreventable/vaccination/immunisationuptak...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
