Screening for Cancer in Patients with Glomerular Diseases
- PMID: 32019761
- PMCID: PMC7274290
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.09000819
Screening for Cancer in Patients with Glomerular Diseases
Keywords: Cancer; cost-benefit analysis; cytosolic phospholipases A2; early detection of cancer; follow-up studies; human PLA2R1 protein; humans; immunosuppressive agents; kidney; membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis; membranous nephropathy; neoplasms; nephrologists; nephrology; nephrotic syndrome; phospholipase A2 receptors; phospholipases A2; recurrence; risk factors; thrombospondins; treatment failure.
Figures
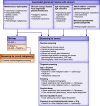
References
-
- Bjørneklett R, Vikse BE, Svarstad E, Aasarød K, Bostad L, Langmark F, Iversen BM: Long-term risk of cancer in membranous nephropathy patients. Am J Kidney Dis 50: 396–403, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Cambier JF, Ronco P: Onco-nephrology: Glomerular diseases with cancer. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7: 1701–1712, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Lefaucheur C, Stengel B, Nochy D, Martel P, Hill GS, Jacquot C, Rossert J; GN-PROGRESS Study Group : Membranous nephropathy and cancer: Epidemiologic evidence and determinants of high-risk cancer association. Kidney Int 70: 1510–1517, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Zaghrini C, Seitz-Polski B, Justino J, Dolla G, Payré C, Jourde-Chiche N, Van de Logt AE, Booth C, Rigby E, Lonnbro-Widgren J, Nystrom J, Mariat C, Cui Z, Wetzels JFM, Ghiggeri G, Beck LH Jr., Ronco P, Debiec H, Lambeau G: Novel ELISA for thrombospondin type 1 domain-containing 7A autoantibodies in membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int 95: 666–679, 2019 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

