Proteomic Profiling of the ECM of Xenograft Breast Cancer Metastases in Different Organs Reveals Distinct Metastatic Niches
- PMID: 32019869
- PMCID: PMC7127975
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2961
Proteomic Profiling of the ECM of Xenograft Breast Cancer Metastases in Different Organs Reveals Distinct Metastatic Niches
Abstract
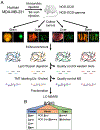
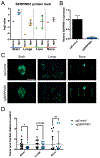
Metastasis causes most cancer-related deaths, and one poorly understood aspect of metastatic cancer is the adaptability of cells from a primary tumor to create new niches and survive in multiple, different secondary sites. We used quantitative mass spectrometry to analyze the extracellular matrix (ECM), a critical component of metastatic niches, in metastases to the brain, lungs, liver, and bone marrow, all derived from parental MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells. Tumor and stromal cells cooperated in forming niches; stromal cells produced predominantly core, structural ECM proteins and tumor cells produced a diverse array of ECM-associated proteins, including secreted factors and modulators of the matrix. In addition, tumor and stromal cells together created distinct niches in each tissue. Downregulation of SERPINB1, a protein elevated in brain metastases, led to a reduction in brain metastasis, suggesting that some niche-specific ECM proteins may be involved in metastatic tropism. SIGNIFICANCE: Tumor and stromal cells together create distinct ECM niches in breast cancer metastases to various tissues, providing new insight into how tumor cells adapt to survive in different tissue environments.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Denkert C, Liedtke C, Tutt A, von Minckwitz G. Molecular alterations in triple-negative breast cancer—the road to new treatment strategies. The Lancet. 2017;389:2430–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

