1RS arm of Secale cereanum 'Kriszta' confers resistance to stripe rust, improved yield components and high arabinoxylan content in wheat
- PMID: 32019962
- PMCID: PMC7000720
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-58419-3
1RS arm of Secale cereanum 'Kriszta' confers resistance to stripe rust, improved yield components and high arabinoxylan content in wheat
Abstract
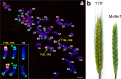
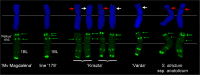
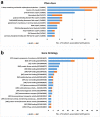
Wheat-rye T1BL.1RS translocation is widespread worldwide as the genes on 1RS arm have positive effect on stress resistance, grain yield and adaptation ability of wheat. Nowadays, the T1BL.1RS wheat cultivars have become susceptible to rust diseases because of the monophyletic ('Petkus') origin of 1RS. Here we report and discuss the production and detailed investigation of a new T1BL.1RS translocation line carrying 1RS with widened genetic base originating from Secale cereanum. Line '179' exhibited improved spike morphology traits, resistance against stripe rust and leaf rust, as well as higher tillering capacity, fertility and dietary fiber (arabynoxylan) content than the parental wheat genotype. Comparative analyses based on molecular cytogenetic methods and molecular (SSR and DArTseq) makers indicate that the 1RS arm of line '179' is a recombinant of S. cereale and S. strictum homologues, and approximately 16% of its loci were different from that of 'Petkus' origin. 162 (69.5%) 1RS-specific markers were associated with genes, including 10 markers with putative disease resistance functions and LRR domains found on the subtelomeric or pericentromeric regions of 1RS. Line '179' will facilitate the map-based cloning of the resistance genes, and it can contribute to healthy eating and a more cost-efficient wheat production.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular cytogenetic characterization of a new wheat-rye 1BL•1RS translocation line expressing superior stripe rust resistance and enhanced grain yield.Planta. 2016 Aug;244(2):405-16. doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2517-3. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Planta. 2016. PMID: 27084678
-
Production and cytomolecular identification of new wheat-perennial rye (Secale cereanum) disomic addition lines with yellow rust resistance (6R) and increased arabinoxylan and protein content (1R, 4R, 6R).Theor Appl Genet. 2016 May;129(5):1045-59. doi: 10.1007/s00122-016-2682-6. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Theor Appl Genet. 2016. PMID: 26883040
-
Development and Characterization of Novel Wheat-Rye 1RS·1BL Translocation Lines with High Resistance to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici.Phytopathology. 2022 Jun;112(6):1310-1315. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-07-21-0313-R. Epub 2022 Apr 28. Phytopathology. 2022. PMID: 34982573
-
Development of a wheat genotype combining the recessive crossability alleles kr1kr1kr2kr2 and the 1BL.1RS translocation, for the rapid enrichment of 1RS with new allelic variation.Theor Appl Genet. 2010 May;120(8):1535-45. doi: 10.1007/s00122-010-1274-0. Epub 2010 Feb 10. Theor Appl Genet. 2010. PMID: 20145905
-
Development and Molecular Cytogenetic Characterization of Novel Primary Wheat-Rye 1RS.1BL Translocation Lines from Multiple Rye Sources with Resistance to Stripe Rust.Plant Dis. 2022 Aug;106(8):2191-2200. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-11-21-2605-RE. Epub 2022 Jul 17. Plant Dis. 2022. PMID: 35077221
Cited by
-
DArTseq genotyping facilitates the transfer of "exotic" chromatin from a Secale cereale × S. strictum hybrid into wheat.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Sep 6;15:1407840. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1407840. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39309182 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide Identification and Evolutionary Analysis of NBS-LRR Genes From Secale cereale.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 9;12:771814. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.771814. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34858486 Free PMC article.
-
Enrichment and Diversification of the Wheat Genome via Alien Introgression.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 23;13(3):339. doi: 10.3390/plants13030339. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting Rye in Wheat Quality Breeding: The Case of Arabinoxylan Content.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 7;12(4):737. doi: 10.3390/plants12040737. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variations of subtelomeric tandem repeats and rDNA on chromosome 1RS arms in the genus Secale and 1BL.1RS translocations.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Apr 25;22(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03598-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35468732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Molnár-Láng, M., Ceoloni, C. & Doležel, J. (eds.). Alien introgression in wheat. Cytogenetics, molecular biology, and genomics / Márta Molnár-Láng, Carla Ceoloni, Jaroslav Doležel, editors (Springer Science + Business Media, Cham, 2015).
-
- Lein, A. Introgression of a rye chromosome to wheat strains by Georg Riebesel-Salzmunde after 1926. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Triticale (EUCARPIA), 158–168 (1975).
-
- Carver BF, Rayburn AL. Comparison of related wheat stocks possessing 1B or 1RS.1BL chromosomes: Agronomic performance. Crop. Sci. 1994;34:1505–1510. doi: 10.2135/cropsci1994.0011183X003400060017x. - DOI
-
- Villareal RL, Bañuelos O, Mujeeb-Kazi A, Rajaram S. Agronomic performance of chromosomes 1B and T1BL.1RS near-isolines in the spring bread wheat Seri M82. Euphytica. 1998;103:195–202. doi: 10.1023/A:1018392002909. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

