Linc00261 inhibits metastasis and the WNT signaling pathway of pancreatic cancer by regulating a miR‑552‑5p/FOXO3 axis
- PMID: 32020223
- PMCID: PMC7041108
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2020.7480
Linc00261 inhibits metastasis and the WNT signaling pathway of pancreatic cancer by regulating a miR‑552‑5p/FOXO3 axis
Abstract
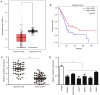
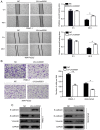
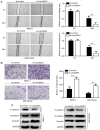
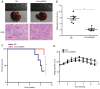
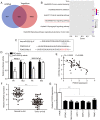
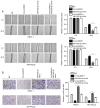
The biological function of long non‑coding RNA00261 (Linc00261) has been widely investigated in various types of cancer. The aim of the present study was to explore the role of Linc00261 in pancreatic cancer (PC). The expression of Linc00261 in patients with PC and PC cell lines was assessed using reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR and the association of Linc00261 expression with survival was analyzed in the online database, GEPIA. The effects of Linc00261 on PC cell metastasis in vitro and in vivo were determined using a wound healing assay, Transwell invasion assays and a nude mouse model of liver metastasis. The relationship between Linc00261, the miR‑552‑5p/forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) axis and the Wnt signaling pathway were determined using bioinformatics analysis, dual luciferase assay and western blotting. Linc00261 expression was significantly decreased in PC tissues and cell lines, and reduced expression was associated with less favorable outcomes in patients with PC. Linc00261 overexpression inhibited migration and invasion of PC cells in vitro, whereas knockdown of Linc00261 increased migration and invasion. Linc00261 overexpression also decreased metastasis of PC cells in vivo. Linc00261 was revealed to directly bind to microRNA (miR)‑552‑5p and to decrease the expression of miR‑552‑5p. In addition, Linc00261 overexpression increased the expression of FOXO3, a target gene of miR‑552‑5p, as well as inhibited the Wnt signaling pathway. Overexpression of miR‑552‑5p in Linc00261‑overexpressing PC cells increased migration and invasion, as well as decreased the expression of FOXO3 and members of the Wnt signaling pathway. Collectively, the present study demonstrated that Linc00261 inhibited metastasis and the Wnt signaling pathway of PC by regulating the miR‑552‑5p/FOXO3 axis. Linc00261 may suppress the development of PC, and serve as a potential biomarker and effective target for the diagnosis and treatment of PC.
Keywords: pancreatic cancer; metastasis; Linc00261; microRNA-552-5p; forkhead box O3.
Figures


References
-
- Lee SH, Chang PH, Chen PT, Lu CH, Hung YS, Tsang NM, Hung CY, Chen JS, Hsu HC, Chen YY, Chou WC. Association of time interval between cancer diagnosis and initiation of palliative chemotherapy with overall survival in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer. Cancer Med. 2019;8:3471–3478. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2254. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Skau Rasmussen L, Vittrup B, Ladekarl M, Pfeiffer P, Karen Yilmaz M, Østergaard Poulsen L, Østerlind K, Palnæs Hansen C, Bau Mortensen M, Viborg Mortensen F, et al. The effect of postoperative gemcitabine on overall survival in patients with resected pancreatic cancer: A nationwide population-based Danish register study. Acta Oncol. 2019;58:864–871. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2019.1581374. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

