Suppression of migration, invasion, and metastasis of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through IKKβ inhibition
- PMID: 32020377
- PMCID: PMC7305835
- DOI: 10.1007/s10585-020-10021-7
Suppression of migration, invasion, and metastasis of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through IKKβ inhibition
Abstract
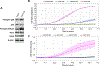
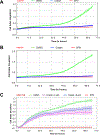
We explored the role of the transcription factor, NF-κB, and its upstream kinase IKKβ in regulation of migration, invasion, and metastasis of cisplatin-resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). We showed that cisplatin-resistant HNSCC cells have a stronger ability to migrate and invade, as well as display higher IKKβ/NF-κB activity compared to their parental partners. Importantly, we found that knockdown of IKKβ, but not NF-κB, dramatically impaired cell migration and invasion in these cells. Consistent with this, the IKKβ inhibitor, CmpdA, also inhibited cell migration and invasion. Previous studies have already shown that N-Cadherin, an epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) marker, and IL-6, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, play important roles in regulation of HNSCC migration, invasion, and metastasis. We found that cisplatin-resistant HNSCC expressed higher levels of N-Cadherin and IL-6, which were significantly inhibited by CmpdA. More importantly, we showed that CmpdA treatment dramatically abated cisplatin-resistant HNSCC cell metastasis to lungs in a mouse model. Our data demonstrated the crucial role of IKKβ in control of migration, invasion, and metastasis, and implicated that targeting IKKβ may be a potential therapy for cisplatin-resistant metastatic HNSCC.
Keywords: Cisplatin resistance; HNSCC; Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; IKKβ; IKKβ inhibitor; Invasion; Metastasis; Migration; NF-κB.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Co-targeting EGFR and IKKβ/NF-κB signalling pathways in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a potential novel therapy for head and neck squamous cell cancer.Br J Cancer. 2019 Feb;120(3):306-316. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0351-z. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Br J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30585254 Free PMC article.
-
A positive feedback loop involving EGFR/Akt/mTORC1 and IKK/NF-kB regulates head and neck squamous cell carcinoma proliferation.Oncotarget. 2016 May 31;7(22):31892-906. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7441. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26895469 Free PMC article.
-
Lupeol suppresses cisplatin-induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and inhibits local invasion and nodal metastasis in an orthotopic nude mouse model.Cancer Res. 2007 Sep 15;67(18):8800-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-0801. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17875721
-
Long non-coding RNAs orchestrate various molecular and cellular processes by modulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021 Nov 1;1867(11):166240. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166240. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021. PMID: 34363933 Review.
-
New advances into cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous carcinoma: Mechanisms and therapeutic aspects.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jul;163:114778. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114778. Epub 2023 May 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37137185 Review.
Cited by
-
Emodin Reverses Gemcitabine Resistance of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines Through Inhibition of IKKβ/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Oct 2;13:9839-9848. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S253691. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33061461 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-infection drug furazolidone inhibits NF-κB signaling and induces cell apoptosis in small cell lung cancer.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020 Dec;36(12):998-1003. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12281. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32767507 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of TRAF2 (rs867186), TAB2 (rs237025), IKBKB (rs13278372) Polymorphisms and TRAF2, TAB2, IKBKB Protein Levels with Clinical and Morphological Features of Pituitary Adenomas.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 10;16(14):2509. doi: 10.3390/cancers16142509. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061149 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) with Cisplatin Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 3;21(11):4002. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114002. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32503307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipase Family Enzymes in Lung Cancer: Looking for Novel Therapeutic Approaches.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 19;15(12):3245. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123245. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, and Jemal A, Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin, 2019. 69(1): p. 7–34. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, et al., Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018. 68(6): p. 394–424. - PubMed
-
- Leemans CR, Braakhuis BJ, and Brakenhoff RH, The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 2011. 11(1): p. 9–22. - PubMed
-
- Braakhuis BJ, Brakenhoff RH, and Leemans CR, Treatment choice for locally advanced head and neck cancers on the basis of risk factors: biological risk factors. Ann Oncol, 2012. 23 Suppl 10: p. x173–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

