Evaluation of two rapid molecular test systems to establish an algorithm for fast identification of bacterial pathogens from positive blood cultures
- PMID: 32020397
- PMCID: PMC7225181
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-020-03828-5
Evaluation of two rapid molecular test systems to establish an algorithm for fast identification of bacterial pathogens from positive blood cultures
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Evaluation of two rapid molecular test systems to establish an algorithm for fast identification of bacterial pathogens from positive blood cultures.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020 Oct;39(10):2003. doi: 10.1007/s10096-020-04012-5. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32870443 Free PMC article.
Abstract
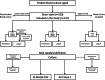
Fast identification of pathogens directly from positive blood cultures is of highest importance to supply an adequate therapy of bloodstream infections (BSI). There are several platforms providing molecular-based identification, detection of antimicrobial resistance genes, or even a full antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST). Two of such test systems allowing rapid diagnostics were assessed in this study: The Biofire FilmArray® and the Genmark ePlex®, both fully automated test system with a minimum of hands-on time. Overall 137 BSI episodes were included in our study and compared to conventional culture-based reference methods. The FilmArray® is using one catridge including a panel for the most common bacterial and fungal BSI pathogens as well as selected resistance markers. The ePlex® offers three different cartridges for detection of Gram-positives, Gram-negatives, and fungi resulting in a broader panel including also rare pathogens, putative contaminants, and more genetic resistance markers. The FilmArray® and ePlex® were evaluated for all 137 BSI episodes with FilmArray® detecting 119 and ePlex® detecting 128 of these. For targets on the respective panel of the system, the FilmArray® generated a sensitivity of 98.9% with 100% specificity on Gram-positive isolates. The ePlex® system generated a sensitivity of 94.7% and a specificity of 90.7% on Gram-positive isolates. In each case, the two systems performed with 100% sensitivity and specificity for the detection of Gram-negative specimens covered by each panel. In summary, both evaluated test systems showed a satisfying overall performance for fast pathogen identification and are beneficial tools for accelerating blood culture diagnostics of sepsis patients.
Keywords: Antibiotic resistance; Biofire FilmArray®; Bloodstream infection; GenMark ePlex®; Molecular identification; Rapid identification system.
Conflict of interest statement
SP received a speakers’ honorarium from Biomerieux (Nürtingen, Germany) and is a consultant for IDbyDNA (San Francisco, USA).
Figures
References
-
- Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK, Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, Angus DC, Reinhart K, International Forum of Acute Care T Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193(3):259–272. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201504-0781OC. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

