Multiparametric radiomics methods for breast cancer tissue characterization using radiological imaging
- PMID: 32020435
- PMCID: PMC7066290
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-020-05533-5
Multiparametric radiomics methods for breast cancer tissue characterization using radiological imaging
Abstract
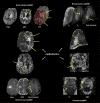
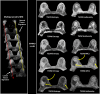
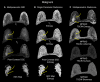
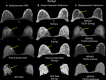
Background and purpose: Multiparametric radiological imaging is vital for detection, characterization, and diagnosis of many different diseases. Radiomics provide quantitative metrics from radiological imaging that may infer potential biological meaning of the underlying tissue. However, current methods are limited to regions of interest extracted from a single imaging parameter or modality, which limits the amount of information available within the data. This limitation can directly affect the integration and applicable scope of radiomics into different clinical settings, since single image radiomics are not capable of capturing the true underlying tissue characteristics in the multiparametric radiological imaging space. To that end, we developed a multiparametric imaging radiomic (mpRad) framework for extraction of first and second order radiomic features from multiparametric radiological datasets.
Methods: We developed five different radiomic techniques that extract different aspects of the inter-voxel and inter-parametric relationships within the high-dimensional multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging breast datasets. Our patient cohort consisted of 138 breast patients, where, 97 patients had malignant lesions and 41 patients had benign lesions. Sensitivity, specificity, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and areas under the curve (AUC) analysis were performed to assess diagnostic performance of the mpRad parameters. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
Results: The mpRad features successfully classified malignant from benign breast lesions with excellent sensitivity and specificity of 82.5% and 80.5%, respectively, with Area Under the receiver operating characteristic Curve (AUC) of 0.87 (0.81-0.93). mpRad provided a 9-28% increase in AUC metrics over single radiomic parameters.
Conclusions: We have introduced the mpRad framework that extends radiomic analysis from single images to multiparametric datasets for better characterization of the underlying tissue biology.
Keywords: ADC; Breast cancer; Diffusion; Entropy; Gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM); Informatics; Machine learning; Magnetic resonance imaging; Multiparametric imaging; Radiomics; Texture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Classification of pulmonary lesion based on multiparametric MRI: utility of radiomics and comparison of machine learning methods.Eur Radiol. 2020 Aug;30(8):4595-4605. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06768-y. Epub 2020 Mar 28. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32222795
-
Multiparametric MRI Radiomics With Machine Learning for Differentiating HER2-Zero, -Low, and -Positive Breast Cancer: Model Development, Testing, and Interpretability Analysis.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2025 Jan;224(1):e2431717. doi: 10.2214/AJR.24.31717. Epub 2024 Oct 16. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2025. PMID: 39413232
-
Magnetic resonance imaging radiomics predicts preoperative axillary lymph node metastasis to support surgical decisions and is associated with tumor microenvironment in invasive breast cancer: A machine learning, multicenter study.EBioMedicine. 2021 Jul;69:103460. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103460. Epub 2021 Jul 4. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34233259 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Radiomics in Breast Imaging from Techniques to Clinical Applications: A Review.Korean J Radiol. 2020 Jul;21(7):779-792. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0855. Korean J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32524780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of radiomics in breast cancer diagnosis and prognostication.Breast. 2020 Feb;49:74-80. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2019.10.018. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Breast. 2020. PMID: 31739125 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated Multiparametric Radiomics and Informatics System for Characterizing Breast Tumor Characteristics with the OncotypeDX Gene Assay.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 27;12(10):2772. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102772. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32992569 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative Prediction Power of Radiomics for Breast Cancer: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 1;12:837257. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.837257. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35299744 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics to Differentiate Malignant and Benign Breast Lesions: A Systematic Review and Diagnostic Test Accuracy Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2023 Nov 18;15(11):e49015. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49015. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38024014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Data Partitioning and Statistical Considerations for Association of Radiomic Features to Biological Underpinnings: What Is Needed.Radiology. 2023 Apr;307(1):e223007. doi: 10.1148/radiol.223007. Epub 2022 Dec 20. Radiology. 2023. PMID: 36537899 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
An updated overview of radiomics-based artificial intelligence (AI) methods in breast cancer screening and diagnosis.Radiol Phys Technol. 2024 Dec;17(4):795-818. doi: 10.1007/s12194-024-00842-6. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Radiol Phys Technol. 2024. PMID: 39285146 Review.
References
-
- Tixier F, Le Rest CC, Hatt M, Albarghach N, Pradier O, Metges J-P, Corcos L, Visvikis D. Intratumor heterogeneity characterized by textural features on baseline 18F-FDG PET images predicts response to concomitant radiochemotherapy in esophageal cancer. J Nucl Med. 2011;52(3):369–378. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.110.082404. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kumar V, Gu Y, Basu S, Berglund A, Eschrich SA, Schabath MB, Forster K, Aerts HJ, Dekker A, Fenstermacher D, Goldgof DB, Hall LO, Lambin P, Balagurunathan Y, Gatenby RA, Gillies RJ. Radiomics: the process and the challenges. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;30(9):1234–1248. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2012.06.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

