S-1 plus cisplatin with concurrent radiotherapy for locally advanced thymic carcinoma: Study protocol of LOGIK1605/JART-1501
- PMID: 32020735
- PMCID: PMC7049479
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.13319
S-1 plus cisplatin with concurrent radiotherapy for locally advanced thymic carcinoma: Study protocol of LOGIK1605/JART-1501
Abstract
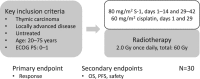
Thymic carcinoma is a rare epithelial tumor of the thymus with a poor prognosis, and multimodal approaches are important for its treatment. Recently, a number of studies have indicated that S-1 treatment is effective against thymic carcinoma. S-1 plus cisplatin with concurrent radiotherapy is a commonly used treatment for other malignancies, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In addition, its safety has been confirmed, and it has been reported to have a marked effect against thymic carcinoma. Therefore, we conducted a phase II study of S-1 plus cisplatin with concurrent thoracic radiotherapy for locally advanced thymic carcinoma, in which the overall response rate was employed as the primary endpoint. The secondary endpoints were overall survival, progression-free survival, and safety.
Keywords: Cisplatin; S-1; radiotherapy; thymic carcinoma.
© 2020 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
References
-
- Bretti S, Berruti A, Loddo C et al Multimodal management of stage III‐IVa malignant thymoma. Lung Cancer 2004; 44: 69–77. - PubMed
-
- Shirasaka T, Nakano K, Takechi T et al Antitumor activity of 1 M tegafur‐0.4 M 5‐chloro‐2,4‐dihydroxypyridine‐1 M potassium oxonate (S‐1) against human colon carcinoma orthotopically implanted into nude rats. Cancer Res 1996; 56: 2602–6. - PubMed
-
- Miyamoto S, Boku N, Ohtsu A et al Clinical implications of immunoreactivity of thymidylate synthase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in gastric cancer treated with oral fluoropyrimidine (S‐1). Study group of S‐1 for gastric cancer. Int J Oncol 2000; 17: 653–8. - PubMed
-
- Ono A, Naito T, Yamamoto N. S‐1 treatment for chemorefractory thymic carcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 2008; 3: 1076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical