Corrosive Ingestion
- PMID: 32021005
- PMCID: PMC6996660
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23305
Corrosive Ingestion
Abstract
Corrosive ingestion remains a common problem in developing countries, such as India due to the lack of strict laws that regulate the sale of caustics. While appropriate treatment of the acute phase can mitigate tissue damage improper management of the acute corrosive injury is widely prevalent due to the limited experience of the individual physicians in managing this condition. The aim of this review is to summarize the epidemiology and pathophysiology of corrosive ingestion, principles in the management of acute phase injury, long-term effects of caustic ingestion, and prevention of corrosive ingestion.
How to cite this article: Kalayarasan R, Ananthakrishnan N, Kate V. Corrosive Ingestion. Indian J Crit Care Med 2019;23(Suppl 4):S282-S286.
Keywords: Caustic injury; Corrosive; Esophageal stricture; Gastric stricture; Poisoning.
Copyright © 2019; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures


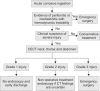
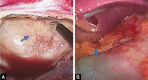
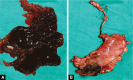
References
-
- Ananthakrishnan N, Kalayarasan R, Kate V. Corrosive injury of esophagus and stomach. In: Mishra PK, editor. Textbook of Surgical Gastroenterology, 1st ed., New Delhi, India: Jaypee; 2016.
-
- Lakshmi CP, Vijayahari R, Kate V, Ananthakrishnan N. A hospital-based epidemiological study of corrosive alimentary injuries with particular reference to the Indian experience. Natl Med J India. 2013;26(1):31–36. - PubMed
-
- Pankaja S, Valooran G, Das S, Suvasini L, Aravind R, Kate V, et al. Isolated full thickness jejunal necrosis following sulphuric acid cocktail ingestion—a clinical case report—isolated corrosive jejunal necrosis. Surg Sci. 2011;2:338–340. doi: 10.4236/ss.2011.26072. DOI: - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
