Curcumin Combined with Thalidomide Reduces Expression of STAT3 and Bcl-xL, Leading to Apoptosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines
- PMID: 32021103
- PMCID: PMC6970263
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S228610
Curcumin Combined with Thalidomide Reduces Expression of STAT3 and Bcl-xL, Leading to Apoptosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines
Abstract
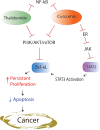
Introduction: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of blood disorder that exhibits uncontrolled growth and reduced ability to undergo apoptosis. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a family member of transcription factors which promotes carcinogenesis in most human cancers. This effect on AML is accomplished through deregulation of several critical genes, such as B cell lymphoma-extra-large (BCL-XL) which is anti-apoptotic protein. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of curcumin (CUR) and thalidomide (THAL) on apoptosis induction and also the alteration of the mRNA expression level of STAT3 and BCL-XL mRNA on AML cell line compounds.
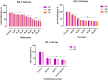
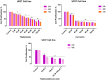
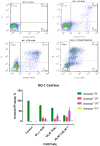
Methods: The growth inhibitory effects of CUR and THAL and their combination were measured by MTT assay in U937 and KG-1 cell lines. The rates of apoptosis induction and cell cycle analysis were measured by concurrent staining with Annexin V and PI. The mRNA expression level of STAT3 and BCL-XL was evaluated by Real-Time PCR.
Results: CUR inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in both KG-1 and U937 cells and this effect increased by combination with THAL. The expression level of STAT3 and BCL-XL was significantly down-regulated in KG-1 cells after treatment by CUR and THAL and their combination.
Conclusion: Overall, our findings suggested that down-regulation of STAT3 and BCL-XL mRNA expression in response to CUR and THAL treatment lead to inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptosis.
Keywords: Bcl-xL; STAT3; acute myeloid leukemia; curcumin; thalidomide.
© 2020 Mohammadi Kian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Curcumin and acute myeloid leukemia: a golden hope, updated insights.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 11;52(1):583. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10692-z. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40498262 Review.
-
[Curcumin Combined with Thalidomide Inhibits Proliferation of KG-1 Cells and Its Related Mechanisms].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Apr;32(2):422-427. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2024.02.015. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38660846 Chinese.
-
Curcumin combined with arsenic trioxide enhances autophagy and immune surveillance to inhibit immune escape in acute myeloid leukemia.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Jun 26;159:114966. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114966. Epub 2025 May 28. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40440957
-
Curcumin reduces expression of Bcl-2, leading to apoptosis in daunorubicin-insensitive CD34+ acute myeloid leukemia cell lines and primary sorted CD34+ acute myeloid leukemia cells.J Transl Med. 2011 May 19;9:71. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-71. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21595920 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting STAT3 signaling pathway by curcumin and its analogues for breast cancer: A narrative review.Animal Model Exp Med. 2024 Dec;7(6):853-867. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12491. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Animal Model Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39219410 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin Derivatives in Medicinal Chemistry: Potential Applications in Cancer Treatment.Molecules. 2024 Nov 12;29(22):5321. doi: 10.3390/molecules29225321. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39598712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Natural Compounds/siRNA Co-delivery Employing Nanovehicles for Cancer Therapy.ACS Comb Sci. 2020 Dec 14;22(12):669-700. doi: 10.1021/acscombsci.0c00099. Epub 2020 Oct 23. ACS Comb Sci. 2020. PMID: 33095554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is Curcumin the Answer to Future Chemotherapy Cocktail?Molecules. 2021 Jul 17;26(14):4329. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144329. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin and acute myeloid leukemia: a golden hope, updated insights.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 11;52(1):583. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10692-z. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40498262 Review.
-
Synergistic effects of thalidomide and cisplatin are mediated via the PI3K/AKT and JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathways in cervical cancer.Oncol Rep. 2022 Oct;48(4):169. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8384. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35920185 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

