Siva 1 Inhibits Cervical Cancer Progression and Its Clinical Prognosis Significance
- PMID: 32021444
- PMCID: PMC6970243
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S232994
Siva 1 Inhibits Cervical Cancer Progression and Its Clinical Prognosis Significance
Abstract
Background: Cervical cancer is the second most common female malignancies. But the exact etiology of cervical cancer is still under investigation. Recent observations revealed that the loss expression of Siva 1 was related to several different types of tumors. It could play an indispensable role in both exogenous and endogenous apoptotic signaling pathways. Nevertheless, the relationship between Siva 1 expression and cervical cancer progression has not yet been fully clarified. This study aimed to explore the functional role of Siva1 in cervical cancer.
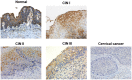
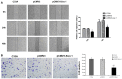
Materials and methods: In this present experiment, expression of Siva 1 was detected in 87 cervical cancer, 34 CIN and 20 normal samples by immunohistochemistry. The correlation of Siva 1 expression and overall survival times (OS) was analyzed by Kaplan-Meier analysis. We up-regulated the expression of Siva 1 by plasmid pCMV3-Siva 1 in C33A cells. CCK8, flow cytometry, wound-healing, and transwell assays were performed to examine the influences of Siva 1 expression on cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion.
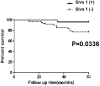
Results: The expression of Siva 1 was decreased in cervical cancer tissues compared with CIN and normal tissues. In addition, the Siva 1 immunoreactivity was significantly associated with tumor differentiation. Patients with Siva 1 negative staining exhibited a significantly decreased overall survival. Then, we established stable Siva 1 ectopic expression cells, and we found that elevated expression of Siva 1 promoted apoptosis, inhibited proliferation, and suppressed migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells.
Conclusion: The present study revealed a crucial role of Siva 1 in tumor progression and it may be a valuable prognostic indicator of cervical cancer.
Keywords: Siva 1; apoptosis; cervical cancer; prognosis; proliferation.
© 2020 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

