Use of a Systematic Pharmacological Methodology to Explore the Mechanism of Shengmai Powder in Treating Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 32023237
- PMCID: PMC7020766
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.919029
Use of a Systematic Pharmacological Methodology to Explore the Mechanism of Shengmai Powder in Treating Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
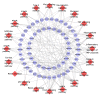
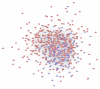
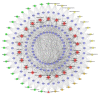
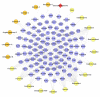
BACKGROUND Cardiovascular complications, such as diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM), are the leading cause of death in diabetic patients. Shengmai Powder (SMP) was found to have cardioprotective effects. MATERIAL AND METHODS Based on the systematic pharmacological methodology, this research determined the genes of DCM and the known targets of SMP, predicted potential compounds and targets of SMP, constructed networks for DCM and SMP, and performed network analysis. RESULTS Five network were constructed: (1) the DCM gene PPI network; (2) the Compound-compound target network of SMP; (3) the SMP-DCM PPI network; (4) the Compound-known target network of SMP; (5) and the SMP known target-DCM PPI network. Several DCM and treatment related targets, clusters, signaling pathways, and biological processes were found. CONCLUSIONS SMP is able to regulate glycometabolism-related, lipid metabolism-related, inflammatory response-related, oxidative stress-related signaling pathways, and biological processes and targets, which suggests that SMP may have a therapeutic effect on DCM.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures






References
-
- Yach D, Stuckler D, Brownell KD. Epidemiologic and economic consequences of the global epidemics of obesity and diabetes. Nat Med. 2006;12:62–66. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. Diabetes statistics. 2011. Available from www.diabetes.org/diabetes-basics/diabetes-statistics/
-
- Anand SS, Yusuf S. Stemming the global tsunami of cardiovascular disease. Lancet. 2011;377:529–32. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

