Use of CAR-Transduced Natural Killer Cells in CD19-Positive Lymphoid Tumors
- PMID: 32023374
- PMCID: PMC7101242
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910607
Use of CAR-Transduced Natural Killer Cells in CD19-Positive Lymphoid Tumors
Abstract
Background: Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has shown remarkable clinical efficacy in B-cell cancers. However, CAR T cells can induce substantial toxic effects, and the manufacture of the cells is complex. Natural killer (NK) cells that have been modified to express an anti-CD19 CAR have the potential to overcome these limitations.
Methods: In this phase 1 and 2 trial, we administered HLA-mismatched anti-CD19 CAR-NK cells derived from cord blood to 11 patients with relapsed or refractory CD19-positive cancers (non-Hodgkin's lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukemia [CLL]). NK cells were transduced with a retroviral vector expressing genes that encode anti-CD19 CAR, interleukin-15, and inducible caspase 9 as a safety switch. The cells were expanded ex vivo and administered in a single infusion at one of three doses (1×105, 1×106, or 1×107 CAR-NK cells per kilogram of body weight) after lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
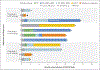
Results: The administration of CAR-NK cells was not associated with the development of cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxicity, or graft-versus-host disease, and there was no increase in the levels of inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-6, over baseline. The maximum tolerated dose was not reached. Of the 11 patients who were treated, 8 (73%) had a response; of these patients, 7 (4 with lymphoma and 3 with CLL) had a complete remission, and 1 had remission of the Richter's transformation component but had persistent CLL. Responses were rapid and seen within 30 days after infusion at all dose levels. The infused CAR-NK cells expanded and persisted at low levels for at least 12 months.
Conclusions: Among 11 patients with relapsed or refractory CD19-positive cancers, a majority had a response to treatment with CAR-NK cells without the development of major toxic effects. (Funded by the M.D. Anderson Cancer Center CLL and Lymphoma Moonshot and the National Institutes of Health; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT03056339.).
Copyright © 2020 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
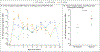
Comment in
-
Cancer Immunotherapy: Make Way for CAR NK.Cancer Discov. 2020 Apr;10(4):484. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-ND2020-004. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 32086314
-
Double boost for cancer cell therapy.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020 Mar;19(3):165. doi: 10.1038/d41573-020-00018-y. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020. PMID: 32127667 No abstract available.
-
Cord Blood CAR-NK Cells: Favorable Initial Efficacy and Toxicity but Durability of Clinical Responses Not Yet Clear.Cancer Cell. 2020 Apr 13;37(4):426-427. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.03.018. Cancer Cell. 2020. PMID: 32289266
-
CAR-Transduced Natural Killer Cells.N Engl J Med. 2020 May 7;382(19):1865-1866. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2004226. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32374974 No abstract available.
-
CAR-Transduced Natural Killer Cells.N Engl J Med. 2020 May 7;382(19):1866. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2004226. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32374975 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
