Monitoring Consumption of Common Illicit Drugs in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, by Wastewater-Cased Epidemiology
- PMID: 32023897
- PMCID: PMC7036889
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17030889
Monitoring Consumption of Common Illicit Drugs in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, by Wastewater-Cased Epidemiology
Abstract
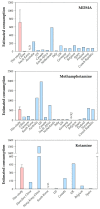
Southeast Asian countries including Malaysia play a major role in global drug trade and abuse. Use of amphetamine-type stimulants has increased in the past decade in Malaysia. This study aimed to apply wastewater-based epidemiology for the first time in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, to estimate the consumption of common illicit drugs in urban population. Influent wastewater samples were collected from two wastewater treatment plants in Kuala Lumpur in the summer of 2017. Concentrations of twenty-four drug biomarkers were analyzed for estimating drug consumption. Fourteen drug residues were detected with concentrations of up to 1640 ng/L. Among the monitored illicit drugs, 3,4-methylenedioxy-methamphetamine (MDMA) or ecstasy had the highest estimated per capita consumptions. Consumption and dose of amphetamine-type stimulants (methamphetamine and MDMA) were both an order of magnitude higher than those of opioids (heroin and codeine, methadone and tramadol). Amphetamine-type stimulants were the most prevalent drugs, replacing opioids in the drug market. The prevalence trend measured by wastewater-based epidemiology data reflected the shift to amphetamine-type stimulants as reported by the Association of Southeast Asian Nations Narcotics Cooperation Center. Most of the undetected drug residues were new psychoactive substances (NPSs), suggesting a low prevalence of NPSs in the drug market.
Keywords: MDMA; Southeast Asia; ketamine; methamphetamine; substance abuse; wastewater analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estimation of the prevalence of substance use by wastewater-based epidemiology study in four cities of Guangdong, China.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 9;20(4):e0320141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320141. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40203000 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the impact of a major electronic music festival on the consumption patterns of illicit and licit psychoactive substances in a Mediterranean city using wastewater analysis.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Sep 20;892:164547. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164547. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 37270014
-
Use of illicit stimulant drugs in Finland: a wastewater study in ten major cities.Sci Total Environ. 2014 Jul 15;487:696-702. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.095. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Sci Total Environ. 2014. PMID: 24331163
-
Wastewater-based epidemiology for illicit drugs: A critical review on global data.Water Res. 2021 Dec 1;207:117789. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2021.117789. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Water Res. 2021. PMID: 34731667 Review.
-
A global systematic review and meta-analysis on illicit drug consumption rate through wastewater-based epidemiology.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Oct;27(29):36037-36051. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09818-6. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32594443
Cited by
-
Estimation of the prevalence of substance use by wastewater-based epidemiology study in four cities of Guangdong, China.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 9;20(4):e0320141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320141. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40203000 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine-associated upper urinary tract dysfunction: What we know from current literature.Asian J Urol. 2025 Jan;12(1):33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ajur.2024.05.004. Epub 2024 Oct 11. Asian J Urol. 2025. PMID: 39990075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring drivers of pre-exposure prophylaxis uptake among gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men in Malaysia.Int J STD AIDS. 2022 Aug;33(9):821-828. doi: 10.1177/09564624221106535. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Int J STD AIDS. 2022. PMID: 35772943 Free PMC article.
-
Substance abuse among new patients attending main government hospitals in Malaysia from 2018-2021: A comparison between before and during COVID-19 pandemic.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 24;19(10):e0309422. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309422. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39446726 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal cord infarction in a young patient with methamphetamine abuse.BMJ Case Rep. 2021 Mar 30;14(3):e241031. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-241031. BMJ Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33785605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNODC (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime) World Drug Report 2018, Executive Summary Conclusions and Policy Implications. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime; Vienna, Austria: 2018.
-
- UNODC (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime) Synthetic Drugs in East and South-East Asia-Trends and Patterns of Amphetamine-Type Stimulants and New Psychoactive Substances. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime; Vienna, Austria: 2019.
-
- UNODC (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime) Transnational Organized Crime in Southeast Asia: Evolution, Growth and Impact. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime; Vienna, Austria: 2019.
-
- UNODC (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime) World Drug Report 2017. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime; Vienna, Austria: 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous