Mechanisms and Alterations of Cardiac Ion Channels Leading to Disease: Role of Ankyrin-B in Cardiac Function
- PMID: 32023981
- PMCID: PMC7072516
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10020211
Mechanisms and Alterations of Cardiac Ion Channels Leading to Disease: Role of Ankyrin-B in Cardiac Function
Abstract
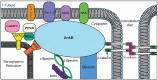
Ankyrin-B (encoded by ANK2), originally identified as a key cytoskeletal-associated protein in the brain, is highly expressed in the heart and plays critical roles in cardiac physiology and cell biology. In the heart, ankyrin-B plays key roles in the targeting and localization of key ion channels and transporters, structural proteins, and signaling molecules. The role of ankyrin-B in normal cardiac function is illustrated in animal models lacking ankyrin-B expression, which display significant electrical and structural phenotypes and life-threatening arrhythmias. Further, ankyrin-B dysfunction has been associated with cardiac phenotypes in humans (now referred to as "ankyrin-B syndrome") including sinus node dysfunction, heart rate variability, atrial fibrillation, conduction block, arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy, structural remodeling, and sudden cardiac death. Here, we review the diverse roles of ankyrin-B in the vertebrate heart with a significant focus on ankyrin-B-linked cell- and molecular-pathways and disease.
Keywords: ANK2; ankyrin-B; cardiovascular disease; ion channels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P.J. Identification and partial purification of ankyrin, the high affinity membrane attachment site for human erythrocyte spectrin. J. Biol. Chem. 1979;254:2533–2541. - PubMed
-
- Davis J.Q., Bennett V. Brain ankyrin. Purification of a 72,000 Mr spectrin-binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1984;259:1874–1881. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

