Exploring the Scope of Macrocyclic "Shoe-last" Templates in the Mechanochemical Synthesis of RHO Topology Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks (ZIFs)
- PMID: 32024141
- PMCID: PMC7037713
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25030633
Exploring the Scope of Macrocyclic "Shoe-last" Templates in the Mechanochemical Synthesis of RHO Topology Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks (ZIFs)
Abstract
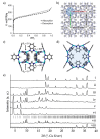
The macrocyclic cavitand MeMeCH2 is used as a template for the mechanochemical synthesis of 0.2MeMeCH2@RHO-Zn16(Cl2Im)32 (0.2MeMeCH2@ZIF-71) and RHO-ZnBIm2 (ZIF-11) zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs). It is shown that MeMeCH2 significantly accelerates the mechanochemical synthesis, providing high porosity products (BET surface areas of 1140 m2/g and 869 m2/g, respectively). Templation of RHO-topology ZIF frameworks constructed of linkers larger than benzimidazole (HBIm) was unsuccessful. It is also shown that cavitands other than MeMeCH2-namely MeHCH2, MeiBuCH2, HPhCH2, MePhCH2, BrPhCH2, BrC5CH2-can serve as effective templates for the synthesis of x(cavitand)@RHO-ZnIm2 products. The limitations on cavitand size and shape are explored in terms of their effectiveness as templates.
Keywords: mechanochemical synthesis; microporous materials; templation; zeolitic imidazolate frameworks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Wu T., Bu X., Zhang J., Feng P. New Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks: From Unprecedented Assembly of Cubic Clusters to Ordered Cooperative Organization of Complementary Ligands. Chem. Mater. 2008;20:7377–7382. doi: 10.1021/cm802400f. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

