Breast cancer in a patient with Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome (BHDS) with dramatic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- PMID: 32024715
- PMCID: PMC7021115
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2019-232226
Breast cancer in a patient with Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome (BHDS) with dramatic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Abstract
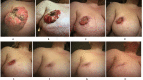
This is a case of 49-year-old white woman who presented with a rapidly growing right sided breast mass. A subsequent punch biopsy confirmed grade 3 invasive mammary carcinoma of no special type which was negative for oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and Her-2 neu overexpression. She was a carrier of folliculin gene mutation that is characteristic of Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome (BHDS), a condition known to cause skin lesions, renal cancers and pneumothoraces. Family history revealed patient's mother, grandmother and maternal aunt developed renal cell carcinomas during their lifetime and were positive for the same germ line mutation. Tumour tissue was positive for TP53 mutation and negative for BRCA1, BRCA2 and other genes commonly associated with breast cancer. We report a patient with BHDS presenting with breast cancer that showed dramatic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy prior to bilateral mastectomy, local chest wall radiation and 6 months of adjuvant capecitabine.
Keywords: breast cancer; cancer - see oncology; cancer intervention; carcinogenesis; radiotherapy.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Leiomyosarcoma in Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2020 Mar;42(2):136-137. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000001715. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31929385
-
Possible familial case of Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome complicated with lung cancer: A possible link between these two disease entities.Respir Med. 2015 Jul;109(7):923-5. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 14. Respir Med. 2015. PMID: 26028485
-
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome and familial adenomatous polyposis: an association or a coincidence?Intern Med. 2012;51(13):1789-92. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.51.7239. Epub 2012 Jul 1. Intern Med. 2012. PMID: 22790147
-
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome with simultaneous hyperplastic polyposis of the gastrointestinal tract: case report and review of the literature.BMC Med Genet. 2020 Mar 14;21(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12881-020-0991-8. BMC Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 32171268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome: Clinical and molecular aspects of recently identified kidney cancer syndrome.Int J Urol. 2016 Mar;23(3):204-10. doi: 10.1111/iju.13015. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Int J Urol. 2016. PMID: 26608100 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
