Probing the function of long noncoding RNAs in the nucleus
- PMID: 32026224
- PMCID: PMC7131881
- DOI: 10.1007/s10577-019-09625-x
Probing the function of long noncoding RNAs in the nucleus
Abstract
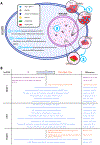
The nucleus is a highly organized and dynamic environment where regulation and coordination of processes such as gene expression and DNA replication are paramount. In recent years, noncoding RNAs have emerged as key participants in the regulation of nuclear processes. There are a multitude of functional roles for long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), mediated through their ability to act as molecular scaffolds bridging interactions with proteins, chromatin, and other RNA molecules within the nuclear environment. In this review, we discuss the diversity of techniques that have been developed to probe the function of nuclear lncRNAs, along with the ways in which those techniques have revealed insights into their mechanisms of action. Foundational observations into lncRNA function have been gleaned from molecular cytology-based, single-cell approaches to illuminate both the localization and abundance of lncRNAs in addition to their potential binding partners. Biochemical, extraction-based approaches have revealed the molecular contacts between lncRNAs and other molecules within the nuclear environment and how those interactions may contribute to nuclear organization and regulation. Using examples of well-studied nuclear lncRNAs, we demonstrate that the emerging functions of individual lncRNAs have been most clearly deduced from combined cytology and biochemical approaches tailored to study specific lncRNAs. As more functional nuclear lncRNAs continue to emerge, the development of additional technologies to study their interactions and mechanisms of action promise to continually expand our understanding of nuclear organization, chromosome architecture, genome regulation, and disease states.
Keywords: Biochemical methods; Genome regulation; Microscopy; Molecular cytology; Noncoding RNA; Nuclear organization.
Figures


References
-
- Amodio N, Stamato MA, Juli G, Morelli E, Fulciniti M, Manzoni M, Taiana E, Agnelli L, Cantafio MEG, Romeo E et al. (2018b). Drugging the lncRNA MALAT1 via LNA gapmeR ASO inhibits gene expression of proteasome subunits and triggers anti-multiple myeloma activity. Leukemia 32, 1948–1957. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amodio N, Stamato MA, Juli G, Morelli E, Fulciniti M, Manzoni M, Taiana E, Agnelli L, Cantafio MEG, Romeo E et al. (2018c). Drugging the lncRNA MALAT1 via LNA gapmeR ASO inhibits gene expression of proteasome subunits and triggers anti-multiple myeloma activity. Leukemia 32, 1948–1957. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ballabio A and Willard HF (1992). Mammalian X-chromosome inactivation and the XIST gene. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2, 439–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

