Aurora B kinase is recruited to multiple discrete kinetochore and centromere regions in human cells
- PMID: 32028528
- PMCID: PMC7055008
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201905144
Aurora B kinase is recruited to multiple discrete kinetochore and centromere regions in human cells
Abstract
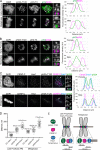
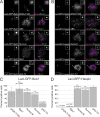
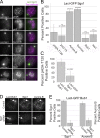
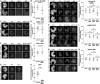
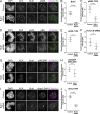
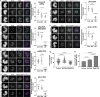
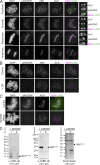
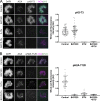
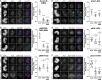
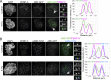
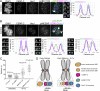
Aurora B kinase has a critical role in regulating attachments between kinetochores and spindle microtubules during mitosis. Early in mitosis, kinase activity at kinetochores is high to promote attachment turnover, and in later mitosis, activity decreases to ensure attachment stabilization. Aurora B localizes prominently to inner centromeres, and a population of the kinase is also detected at kinetochores. How Aurora B is recruited to and evicted from these regions to regulate kinetochore-microtubule attachments remains unclear. Here, we identified and investigated discrete populations of Aurora B at the centromere/kinetochore region. An inner centromere pool is recruited by Haspin phosphorylation of histone H3, and a kinetochore-proximal outer centromere pool is recruited by Bub1 phosphorylation of histone H2A. Finally, a third pool resides ~20 nm outside of the inner kinetochore protein CENP-C in early mitosis and does not require either the Bub1/pH2A/Sgo1 or Haspin/pH3 pathway for localization or activity. Our results suggest that distinct molecular pathways are responsible for Aurora B recruitment to centromeres and kinetochores.
© 2020 Broad et al.
Figures
References
-
- Baron A.P., von Schubert C., Cubizolles F., Siemeister G., Hitchcock M., Mengel A., Schröder J., Fernández-Montalván A., von Nussbaum F., Mumberg D., and Nigg E.A.. 2016. Probing the catalytic functions of Bub1 kinase using the small molecule inhibitors BAY-320 and BAY-524. eLife. 5:e12187 10.7554/eLife.12187 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

