Dietary methylsulfonylmethane supplementation and oxidative stress in broiler chickens
- PMID: 32029168
- PMCID: PMC7587734
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.12.010
Dietary methylsulfonylmethane supplementation and oxidative stress in broiler chickens
Abstract
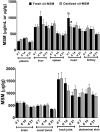
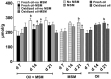
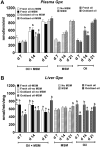
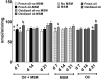
Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) is an organic, sulfur-containing compound widely used as a dietary supplement to improve joint health and treat arthritic pain. An experiment was conducted to study the effects of feeding 0.05% MSM to broilers exposed to diet-induced oxidative stress on tissue MSM distribution, growth performance, oxidative stress biomarkers, and immune responsivity. A total of 528 birds were allocated to 4 dietary treatments (fresh oil-no MSM, fresh oil-MSM, oxidized oil-no MSM, oxidized oil-MSM) as provided ad libitum to 11 replicate cages of 12 birds per treatment. Blood and tissue samples were collected to analyze MSM concentrations, and oxidative stress biomarkers including concentrations of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), total glutathione, and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) and reductase (GR) activities. Additionally, blood samples collected at day 25 were used to quantify T-cell (TC) populations using flow cytometry. Overall, MSM was quantified in all tissues and plasma samples of MSM-treated groups at all time points. Oxidized oil reduced (P = 0.006) feed intake over the 21-d feeding period, but MSM did not affect growth equally across time points. No effects (P > 0.2) of MSM or oil type were observed on TC populations. In the presence of oxidized oil, MSM reduced (P = 0.013) plasma TBARS and increased (P = 0.02) liver GPx at day 21, and increased (P = 0.06) liver GR at day 7. Irrespective of dietary oil type, groups supplemented with MSM showed higher plasma TAC at day 7 (P = 0.023), liver GPx activity at day 21 (P = 0.003), and liver GR activity at day 7 (P = 0.004) compared with groups not receiving MSM. In conclusion, 0.05% dietary MSM supplementation partially protected birds from oxidative stress but did not affect immune cell profiles.
Keywords: MSM; TBARS; broiler; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of methylsulfonylmethane and neutralizing anti-IL-10 antibody supplementation during a mild Eimeria challenge infection in broiler chickens.Poult Sci. 2020 Dec;99(12):6559-6568. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.09.046. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 33248571 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary methyl sulfonyl methane (MSM) supplementation on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, meat quality, excreta microbiota, excreta gas emission, and blood profiles in broilers.Poult Sci. 2017 Jul 1;96(7):2168-2175. doi: 10.3382/ps/pew480. Poult Sci. 2017. PMID: 28339708
-
Oil source and peroxidation status interactively affect growth performance and oxidative status in broilers from 4 to 25 d of age.Poult Sci. 2019 Apr 1;98(4):1749-1761. doi: 10.3382/ps/pey547. Poult Sci. 2019. PMID: 30535333
-
Methylsulfonylmethane: Applications and Safety of a Novel Dietary Supplement.Nutrients. 2017 Mar 16;9(3):290. doi: 10.3390/nu9030290. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28300758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Dietary Methyl Sulfonyl Methane in Poultry.Animals (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;13(3):351. doi: 10.3390/ani13030351. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766239 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Incorporation of Dietary Methyl Sulfonyl Methane into the Egg Albumens of Laying Hens.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Mar 8;11(3):517. doi: 10.3390/antiox11030517. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326167 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of methylsulfonylmethane and neutralizing anti-IL-10 antibody supplementation during a mild Eimeria challenge infection in broiler chickens.Poult Sci. 2020 Dec;99(12):6559-6568. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.09.046. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 33248571 Free PMC article.
-
Additive Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Zeolite and Methyl-Sulfonyl-Methane on Growth Performance and Interleukin Levels of Broiler Chickens.J Poult Sci. 2023 Jan 25;60(1):2023003. doi: 10.2141/jpsa.2023003. J Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 36756049 Free PMC article.
-
Methylsulfonylmethane ameliorates inflammation via NF-κB and ERK/JNK-MAPK signaling pathway in chicken trachea and HD11 cells during Mycoplasma gallisepticum infection.Poult Sci. 2022 Apr;101(4):101706. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101706. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 35121233 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Total Antioxidant Capacity in Serum of Heathy and Stressed Hens.Animals (Basel). 2020 Nov 3;10(11):2019. doi: 10.3390/ani10112019. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33152995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Açıkgöz Z., Bayraktar H., Altan Ö, Akhisaroglu S.T., Kırkpınar F., Altun Z. The effects of moderately oxidised dietary oil with or without vitamin E supplementation on performance, nutrient digestibility, some blood traits, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defense of male broilers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011;91:1277–1282. - PubMed
-
- Altan Ö, Pabuçcuoğlu A., Altan A., Konyalioğlu S., Bayraktar H. Effect of heat stress on oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation and some stress parameters in broilers. Brit. Poult. Sci. 2003;44:545–550. - PubMed
-
- Amirshahrokhi K., Khalili A.R. Methylsulfonylmethane is effective against gastric mucosal injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017;811:240–248. - PubMed
-
- Avanzo J.L., de Mendonça C.X., Jr., Pugine S.M.P., de Cerqueira Cesar M. Effect of vitamin E and selenium on resistance to oxidative stress in chicken superficial pectoralis muscle. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001;129:163–173. - PubMed
-
- Barmaki S., Bohlooli S., Khoshkhahesh F., Nakhostin-Roohi B. Effect of methylsulfonylmethane supplementation on exercise—induced muscle damage and total antioxidant capacity. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness. 2012;52:170. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

