An AMPK-caspase-6 axis controls liver damage in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 32029622
- PMCID: PMC8012106
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aay0542
An AMPK-caspase-6 axis controls liver damage in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
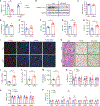
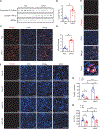
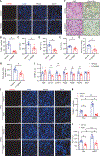
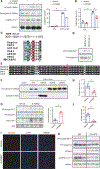
Liver cell death has an essential role in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). The activity of the energy sensor adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is repressed in NASH. Liver-specific AMPK knockout aggravated liver damage in mouse NASH models. AMPK phosphorylated proapoptotic caspase-6 protein to inhibit its activation, keeping hepatocyte apoptosis in check. Suppression of AMPK activity relieved this inhibition, rendering caspase-6 activated in human and mouse NASH. AMPK activation or caspase-6 inhibition, even after the onset of NASH, improved liver damage and fibrosis. Once phosphorylation was decreased, caspase-6 was activated by caspase-3 or -7. Active caspase-6 cleaved Bid to induce cytochrome c release, generating a feedforward loop that leads to hepatocyte death. Thus, the AMPK-caspase-6 axis regulates liver damage in NASH, implicating AMPK and caspase-6 as therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
AMPK against NASH.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Apr;21(4):181. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0225-0. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32071435 No abstract available.
-
The Metabolic Sensor Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Regulates Apoptosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Hepatology. 2020 Sep;72(3):1139-1141. doi: 10.1002/hep.31294. Hepatology. 2020. PMID: 32342535 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK120714/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL143277/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK120515/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK106419/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076906/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL143277/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK060597/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK117551/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

