A selective androgen receptor modulator SARM-2f activates androgen receptor, increases lean body mass, and suppresses blood lipid levels in cynomolgus monkeys
- PMID: 32030892
- PMCID: PMC7005530
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.563
A selective androgen receptor modulator SARM-2f activates androgen receptor, increases lean body mass, and suppresses blood lipid levels in cynomolgus monkeys
Abstract
SARM-2f a selective androgen receptor (AR) modulator, increases skeletal muscle mass and locomotor activity in rats. This study aimed to clarify its pharmacological effects in monkeys. In reporter assays, the EC50 values of SARM-2f for rat, monkey, and human AR were 2.5, 3, and 3.6 nmol/L, respectively; those of testosterone were 12, 3.2, and 11 nmol/L, respectively. A single oral administration (10 mg/kg SARM-2f) produced a maximal plasma concentration of 3011 ng/mL, with an area under the 24 hours concentration-time curve of 8152 ng·h/mL in monkeys. Body weight (BW), lean body mass (LBM), and plasma levels of total cholesterol, triglyceride, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, lipoprotein (a), alanine aminotransferase, and asparagine aminotransferase were measured after 4 weeks of treatment with SARM-2f (1, 3, and 10 mg/kg/day, QD, p.o.) or testosterone enanthate (TE; 2 mg/kg/2 weeks, s.c.) in monkeys. BW and LBM were significantly increased by 12% each by SARM-2f at 10 mg/kg, and by 5% and 8%, respectively, by TE, but these effects were not statistically significant. Plasma levels of all lipids were either decreased or showed a tendency to be decreased by SARM-2f. TE decreased the triglyceride level and increased the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level. Liver marker levels were not changed by either SARM-2f or TE. Our data demonstrated that SARM-2f exerted anabolic effects and produced a lipid profile that differed from that produced by testosterone in monkeys, suggesting that SARM-2f might be useful for diseases such as sarcopenia.
Keywords: body weight; cholesterol; lean body mass; monkey; sarcopenia; selective androgen receptor modulator; testosterone.
© 2020 The Authors. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd, British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to the content of this article.
Figures
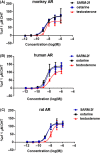

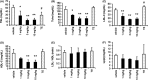

References
-
- Bruggeman AR, Kamal AH, LeBlanc TW, Ma JD, Baracos VE, Roeland EJ. Cancer cachexia: Beyond weight loss. J Oncol Pract. 2016;12:1171‐1174. - PubMed
-
- Cruz‐Jentoft AJ, Sayer AA. Sarcopenia. The Lancet. 2019;393:2636‐2646. - PubMed
-
- Dent E, Morley JE, Cruz‐Jentoft AJ, et al. International clinical practice guidelines for sarcopenia (ICFSR): screening, diagnosis and management. J Nutr Health Aging. 2018;22:114‐161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

