MK-2206 and Standard Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Improves Response in Patients With Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive and/or Hormone Receptor-Negative Breast Cancers in the I-SPY 2 Trial
- PMID: 32031889
- PMCID: PMC7106976
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.19.01027
MK-2206 and Standard Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Improves Response in Patients With Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive and/or Hormone Receptor-Negative Breast Cancers in the I-SPY 2 Trial
Abstract
Purpose: The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin is a key pathway of survival and therapeutic resistance in breast cancer. We evaluated the pan-Akt inhibitor MK-2206 in combination with standard therapy in patients with high-risk early-stage breast cancer.
Patients and methods: I-SPY 2 is a multicenter, phase II, open-label, adaptively randomized neoadjuvant platform trial that screens experimental therapies and efficiently identifies potential predictive biomarker signatures. Patients are categorized by human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), hormone receptor (HR), and MammaPrint statuses in a 2 × 2 × 2 layout. Patients within each of these 8 biomarker subtypes are adaptively randomly assigned to one of several experimental therapies, including MK-2206, or control. Therapies are evaluated for 10 biomarker signatures, each of which is a combination of these subtypes. The primary end point is pathologic complete response (pCR). A therapy graduates with one or more of these signatures if and when it has an 85% Bayesian predictive probability of success in a hypothetical phase III trial, adjusting for biomarker covariates. Patients in the current report received standard taxane- and anthracycline-based neoadjuvant therapy without (control) or with oral MK-2206 135 mg/week.
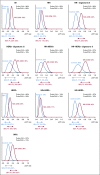
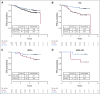
Results: MK-2206 graduated with 94 patients and 57 concurrently randomly assigned controls in 3 graduation signatures: HR-negative/HER2-positive, HR-negative, and HER2-positive. Respective Bayesian mean covariate-adjusted pCR rates and percentage probability that MK-2206 is superior to control were 0.48:0.29 (97%), 0.62:0.36 (99%), and 0.46:0.26 (94%). In exploratory analyses, MK-2206 evinced a numerical improvement in event-free survival in its graduating signatures. The most significant grade 3-4 toxicity was rash (14% maculopapular, 8.6% acneiform).
Conclusion: The Akt inhibitor MK-2206 combined with standard neoadjuvant therapy resulted in higher estimated pCR rates in HR-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer. Although MK-2206 is not being further developed at this time, this class of agents remains of clinical interest.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01042379.
Figures

References
-
- Cortazar P, Geyer CE., Jr Pathological complete response in neoadjuvant treatment of breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:1441–1446. - PubMed
-
- Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M, et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: The CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet. 2014;384:164–172. - PubMed
-
- Prowell TM, Pazdur R. Pathological complete response and accelerated drug approval in early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2438–2441. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

