The cereus matter of Bacillus endophthalmitis
- PMID: 32032628
- PMCID: PMC7113113
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2020.107959
The cereus matter of Bacillus endophthalmitis
Abstract
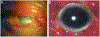
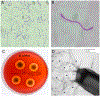
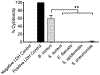
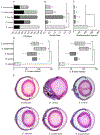
Bacillus cereus (B. cereus) endophthalmitis is a devastating intraocular infection primarily associated with post-traumatic injuries. The majority of these infections result in substantial vision loss, if not loss of the eye itself, within 12-48 h. Multifactorial mechanisms that lead to the innate intraocular inflammatory response during this disease include the combination of robust bacterial replication, migration of the organism throughout the eye, and toxin production by the organism. Therefore, the window of therapeutic intervention in B. cereus endophthalmitis is quite narrow compared to that of other pathogens which cause this disease. Understanding the interaction of bacterial and host factors is critical in understanding the disease and formulating more rational therapeutics for salvaging vision. In this review, we will discuss clinical and research findings related to B. cereus endophthalmitis in terms of the organism's virulence and inflammogenic potential, and strategies for improving of current therapeutic regimens for this blinding disease.
Keywords: Bacillus; Bacteria; Endophthalmitis; Infection; Inflammation; Microbiology.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors report no proprietary or commercial interest in any product mentioned or concept discussed in this article.
Figures
References
-
- Aarthi P, Bagyalakshmi R, Therese KL, Malathi J, Mahalakshmi B, Madhavan HN, 2012. Optimization and application of a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction to determine the bacterial viability in infectious endophthalmitis. Curr. Eye. Res 37, 1114–1120. 10.3109/02713683.2012.704476. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abu el-Asrar AM, al-Amro SA, al-Mosallam AA, al-Obeidan S, 1999. Post-traumatic endophthalmitis: Causative organisms and visual outcome. Eur. J. Ophthalmol 9, 21–31. - PubMed
-
- Affeldt JC, Flynn HW Jr., Forster RK, Mandelbaum S, Clarkson JG, Jarus GD, 1987. Microbial endophthalmitis resulting from ocular trauma. Ophthalmology 94, 407–413. - PubMed
-
- Agaisse H, Gominet M, Okstad OA, Kolsto AB, Lereclus D, 1999. PlcR is a pleiotropic regulator of extracellular virulence factor gene expression in Bacillus thuringiensis. Mol. Microbiol 32, 1043–1053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

