Design and Synthesis of a Compound Library Exploiting 5-Methoxyleoligin as Potential Cholesterol Efflux Promoter
- PMID: 32033108
- PMCID: PMC7038131
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25030662
Design and Synthesis of a Compound Library Exploiting 5-Methoxyleoligin as Potential Cholesterol Efflux Promoter
Abstract
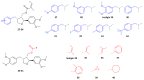
5-Methoxyleoligin and leoligin are natural occurring lignans derived from Edelweiss (Leontopodium nivale ssp. alpinum), displaying potent pro-angiogenic and pro-arteriogenic activity. Cholesterol efflux from macrophages is associated with reverse cholesterol transport which inhibits the development of cardiovascular disease. Within this study, we developed a modular and stereoselective total synthesis of 5-methoxyleoligin which can be readily used to prepare a novel compound library of related analogs. The target 5-methoxyleoligin was synthesized exploiting a recently disclosed modular route, which allows also rapid synthesis of analogous compounds. All obtained products were tested towards macrophage cholesterol efflux enhancement and the performance was compared to the parent compound leoligin. It was found that variation on the aryl moiety in 2-position of the furan ring allows optimization of the activity profile, whereas the ester-functionality does not tolerate significant alterations.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; lignans; macrophage cholesterol efflux; natural product synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Global Health Observatory (GHO) Data. [(accessed on 3 February 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/gho/mortality_burden_disease/causes_death/top_10/en.
-
- Atanasov A.G., Waltenberger B., Pferschy-Wenzig E.M., Linder T., Wawrosch C., Uhrin P., Temml V., Wang L., Schwaiger S., Heiss E.H., et al. Discovery and resupply of pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015;33:1582–1614. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

