Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Senescent Fibroblasts Attenuate the Dermal Effect on Keratinocyte Differentiation
- PMID: 32033114
- PMCID: PMC7037765
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21031022
Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Senescent Fibroblasts Attenuate the Dermal Effect on Keratinocyte Differentiation
Abstract
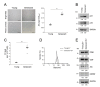
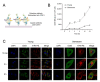
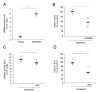
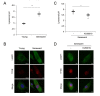
The skin is a multilayered and primary defensive organ. Intimate intercellular communication in the skin is necessary to ensure effective surveillance. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are being explored for their involvement in intercellular skin communication. The aim of this study was to evaluate how human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) accelerate EV production during senescence and the effects of senescence-associated EVs on epidermal homeostasis. Replicative senescent HDFs were assessed with senescence-associated β-galactosidase staining and the expression of senescence-related markers. Isolated EVs were characterized by dynamic light scattering and EV marker expression. EVs secreted from untreated young or senescent HDFs, or from those treated with a nSMase inhibitor, antioxidant, and lysosomal activity regulators, were determined by sandwich ELISA for CD81. Human epidermal keratinocytes were treated with young- and senescent HDF-derived EVs. Compared to young HDFs, senescent HDFs produced relatively high levels of EVs due to the increased nSMase activity, oxidative stress, and altered lysosomal activity. The nSMase inhibitor, antioxidant, and agents that recovered lysosomal activity reduced EV secretion in senescent HDFs. Relative to young HDF-derived EVs, senescent HDF-derived EVs were less supportive in keratinocyte differentiation and barrier function but increased proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 levels. Our study suggests that dermis-derived EVs may regulate epidermal homeostasis by reflecting cellular status, which provides insight as to how the dermis communicates with the epidermis and influences skin senescence.
Keywords: epidermal homeostasis; exosome; extracellular vesicle; human dermal fibroblast; lysosomal activity; senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of Amorepacific Corporation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Human Skin: Cross-Talk from Senescent Fibroblasts to Keratinocytes by miRNAs.J Invest Dermatol. 2019 Dec;139(12):2425-2436.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2019.05.015. Epub 2019 Jun 18. J Invest Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 31220456
-
Reduction of senescence-associated secretory phenotype and exosome-shuttled miRNAs by Haritaki fruit extract in senescent dermal fibroblasts.Int J Cosmet Sci. 2023 Aug;45(4):488-499. doi: 10.1111/ics.12858. Epub 2023 May 7. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36940283
-
Novel mechanisms of sublethal oxidant toxicity: induction of premature senescence in human fibroblasts confers tumor promoter activity.Exp Cell Res. 2003 Oct 15;290(1):38-48. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(03)00308-2. Exp Cell Res. 2003. PMID: 14516786
-
Emerging role of extracellular vesicles as a senescence-associated secretory phenotype: Insights into the pathophysiology of lung diseases.Mol Aspects Med. 2018 Apr;60:92-103. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Mol Aspects Med. 2018. PMID: 29146100 Review.
-
Characteristics and roles of extracellular vesicles released by epidermal keratinocytes.J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019 Dec;33(12):2264-2272. doi: 10.1111/jdv.15859. Epub 2019 Sep 9. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2019. PMID: 31403744 Review.
Cited by
-
Panax ginseng-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Facilitate Anti-Senescence Effects in Human Skin Cells: An Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Way to Use Ginseng Substances.Cells. 2021 Feb 24;10(3):486. doi: 10.3390/cells10030486. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33668388 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Senescence and Its Impact on Angiogenesis in Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 12;24(14):11344. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411344. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin Aging, Cellular Senescence and Natural Polyphenols.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 23;22(23):12641. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312641. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surfaceome analysis of extracellular vesicles from senescent cells uncovers uptake repressor DPP4.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Oct 24;120(43):e2219801120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2219801120. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37862381 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Facial Aesthetics: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 16;23(12):6742. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126742. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743181 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barbieri J.S., Wanat K., Seykora J. Skin: Basic Structure and Function in Pathobiology of Human Disease. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2014. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

