Protective Effects of Sulforaphane on Exercise-Induced Organ Damage via Inducing Antioxidant Defense Responses
- PMID: 32033211
- PMCID: PMC7070986
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9020136
Protective Effects of Sulforaphane on Exercise-Induced Organ Damage via Inducing Antioxidant Defense Responses
Abstract
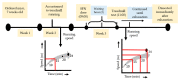
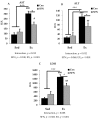
Regular exercise is beneficial to maintain a healthy lifestyle, but the beneficial effects are lost in the case of acute exhaustive exercise; this causes significant inflammation, oxidative stress along with organ damage. Recently, sulforaphane (SFN), an indirect antioxidant, has drawn special attention for its potential protective effect against inflammation and oxidative stress. However, no studies have been performed regarding acute exhaustive exercise-induced organ damage in association with SFN administration. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the effects of SFN on acute exhaustive exercise-induced organ damage and the mechanisms involved. To perform the study, we divided mice into four groups: Control, SFN, exercise, and SFN plus exercise. The SFN group was administered orally (50 mg/kg body wt) 2 h before the running test. We measured plasma levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and acute exhaustive exercise significantly increased these biomarkers. In addition, the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α, were significantly increased in the liver of exercise group. However, the SFN plus exercise group showed a significant reduction in the expression of cytokines and blood biomarkers of tissue damage or cell death. Furthermore, we measured mRNA expression of Nrf2, heme oxygenase (HO)-1, and antioxidant defense enzymes expression, i.e., superoxide dismutase (SOD1), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx1) in the liver. The expression of all these biomarkers was significantly upregulated in the SFN plus exercise group. Collectively, SFN may protect the liver from exhaustive exercise-induced inflammation via inducing antioxidant defense response through the activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signal transduction pathway.
Keywords: Nrf2; antioxidant; antioxidant enzymes; cytokines; exercise; inflammation; oxidative stress; sulforaphane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

