Oropharyngeal Colostrum Positively Modulates the Inflammatory Response in Preterm Neonates
- PMID: 32033312
- PMCID: PMC7071247
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12020413
Oropharyngeal Colostrum Positively Modulates the Inflammatory Response in Preterm Neonates
Abstract
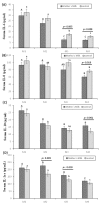
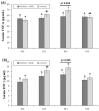
During the first days of life, premature infants have physiological difficulties swallowing, thereby missing out on the benefits of breastfeeding. The aim of this study is to assess the effects of oropharyngeal mother's milk administration in the inflammatory signaling of extremely premature infants. Neonates (n = 100) (<32 week's gestation and/or <1500 g) were divided into two groups: mother's milk group (n = 48), receiving 0.2 mL of oropharyngeal mother's milk every 4 h for the first 15 days of life, and a control group (n = 52), not receiving oropharyngeal mother's milk. Serum concentrations of interleukin (IL) IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-1ra, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and interferón gamma (IFN-γ) were assessed at 1, 3, 15, and 30 days of postnatal life. Maternal and neonatal outcomes were collected. The rate of common neonatal morbidities in both groups was similar. The mother's milk group achieved full enteral feeding earlier, and showed a decrease in Il-6 on days 15 and 30, in IL-8 on day 30, and in TNF-α and INF-γ on day 15, as well as an increase in IL-1ra on days 3 and 15 and in IL-10 on day 30. Oropharyngeal mother's milk administration for 15 days decreases the pro-inflammatory state of preterm neonates and provides full enteral nutrition earlier, which could have a positive influence on the development of the immune system and inflammatory response, thereby positively influencing other developmental outcomes.
Keywords: clinical outcomes; colostrum administration; inflammation; premature neonates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oropharyngeal administration of mother's colostrum, health outcomes of premature infants: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2015 Oct 12;16:453. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0969-6. Trials. 2015. PMID: 26458907 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oropharyngeal Mother's Milk: State of the Science and Influence on Necrotizing Enterocolitis.Clin Perinatol. 2019 Mar;46(1):77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.clp.2018.09.005. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Clin Perinatol. 2019. PMID: 30771821 Review.
-
Enhancement of immune response mediated by oropharyngeal colostrum administration in preterm neonates.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2019 Mar;30(2):234-241. doi: 10.1111/pai.13008. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30444546
-
A pilot study to determine the safety and feasibility of oropharyngeal administration of own mother's colostrum to extremely low-birth-weight infants.Adv Neonatal Care. 2010 Aug;10(4):206-12. doi: 10.1097/ANC.0b013e3181e94133. Adv Neonatal Care. 2010. PMID: 20697221 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrition, growth, and allergic diseases among very preterm infants after hospital discharge.Dan Med J. 2013 Feb;60(2):B4588. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23461996 Review.
Cited by
-
Colostrum oropharyngeal immunotherapy for very low birth weight preterm infants: protocol of an intervention study.BMC Pediatr. 2020 Aug 7;20(1):371. doi: 10.1186/s12887-020-02266-8. BMC Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32767992 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lactoferrin and Immunoglobulin Concentrations in Milk of Gestational Diabetic Mothers.Nutrients. 2021 Mar 2;13(3):818. doi: 10.3390/nu13030818. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33801292 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Application of Mother's Own Milk for Reducing Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Infants: An Updated Meta-Analysis of RCTs.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Apr 7;2023:7378064. doi: 10.1155/2023/7378064. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 37064945 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Prophylactic Effect of Bovine Colostrum on Intestinal Barrier Function in Zonulin Transgenic Mice: A Transcriptomic Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 29;24(19):14730. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914730. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834178 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Outcomes of Early Oral Colostrum Administration in VLBW Neonates: An Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2024 Jan 23;38:7. doi: 10.47176/mjiri.38.7. eCollection 2024. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2024. PMID: 38434229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Romero R., Miranda J., Chaiworapongsa T., Korzeniewski S.J., Chaemsaithong P., Gotsch F., Dong Z., Ahmed A.I., Yoon B.H., Hassan S.S., et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of sterile intra-amniotic inflammation in patients with preterm labor and intact membranes. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2014;72:458–474. doi: 10.1111/aji.12296. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iliodromiti Z., Zygouris D., Sifakis S., Pappa K.I., Tsikouras P., Salakos N., Daniilidis A., Siristatidis C., Vrachnis N. Acute lung injury in preterm fetuses and neonates: Mechanisms and molecular pathways. J. Matern-Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013;26:1696–1704. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2013.798284. - DOI - PubMed

