Dexamethasone Treatment Increases the Intracellular Calcium Level Through TRPV6 in A549 Cells
- PMID: 32033337
- PMCID: PMC7037905
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21031050
Dexamethasone Treatment Increases the Intracellular Calcium Level Through TRPV6 in A549 Cells
Abstract
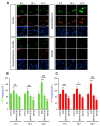
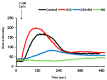
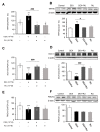
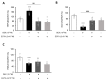
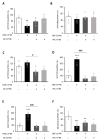
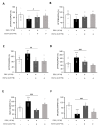
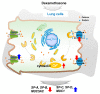
This study investigated the effect of dexamethasone (DEX) on intracellular calcium levels and the expressions of transient receptor potential cation channel subcomponent V member 6 (TRPV6), sodium-calcium exchanger 1 (NCX1), and plasma membrane calcium ATPase 1 (PMCA1) in A549 cells. The intracellular calcium level, by using the calcium indicator pGP-CMV-GCaMP6f, increased following DEX treatment for 6, 12, and 24 h in A549 cells. In addition, Rhod-4 assay after DEX treatment for 24 h showed that DEX increased the level of intracellular calcium. The expression of the calcium influx TRPV6 gene significantly increased, whereas the expressions of the calcium outflow NCX1 and PMCA1 genes significantly decreased with DEX treatment. The mRNA levels of surfactant protein genes SFTPA1, SFTPB, SFTPC, and SFTPD and the secreted airway mucin genes MUC1 and MUC5AC were investigated by treating cells with DEX. The DEX treatment decreased the mRNA levels of SFTPA1 and SFTPB but increased the mRNA levels of SFTPC and SFTPD. The MUC1 mRNA level was increased by DEX treatment, whereas MUC5AC mRNA was significantly decreased. These results indicate that DEX influences the intracellular calcium level through TRPV6, and affects pulmonary surfactant genes and secreted airway mucin genes in A549 cells.
Keywords: A549 cells; TRPV6; calcium; dexamethasone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Raphaël M., Lehen’kyi V., Vandenberghe M., Beck B., Khalimonchyk S., Vanden Abeele F., Farsetti L., Germain E., Bokhobza A., Mihalache A., et al. TRPV6 calcium channel translocates to the plasma membrane via Orai1-mediated mechanism and controls cancer cell survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:E3870–E3879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1413409111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

