Isolation of an Anti-Tumour Disintegrin: Dabmaurin-1, a Peptide Lebein-1-Like, from Daboia mauritanica Venom
- PMID: 32033352
- PMCID: PMC7076848
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12020102
Isolation of an Anti-Tumour Disintegrin: Dabmaurin-1, a Peptide Lebein-1-Like, from Daboia mauritanica Venom
Abstract
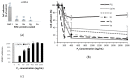
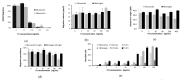
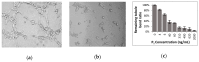
In the soft treatment of cancer tumours, consequent downregulation of the malignant tissue angiogenesis constitutes an efficient way to stifle tumour development and metastasis spreading. As angiogenesis requires integrin-promoting endothelial cell adhesion, migration, and vessel tube formation, integrins represent potential targets of new therapeutic anti-angiogenic agents. Our work is a contribution to the research of such therapeutic disintegrins in animal venoms. We report isolation of one peptide, named Dabmaurin-1, from the hemotoxic venom of snake Daboia mauritanica, and we evaluate its potential anti-tumour activity through in vitro inhibition of the human vascular endothelial cell HMECs functions involved in tumour angiogenesis. Dabmaurin-1 altered, in a dose-dependent manner, without any significant cytotoxicity, HMEC proliferation, adhesion, and their mesenchymal migration onto various extracellular matrix proteins, as well as formation of capillary-tube mimics on MatrigelTM. Via experiments involving HMEC or specific cancers cells integrins, we demonstrated that the above Dabmaurin-1 effects are possibly due to some anti-integrin properties. Dabmaurin-1 was demonstrated to recognize a broad panel of prooncogenic integrins (αvβ6, αvβ3 or αvβ5) and/or particularly involved in control of angiogenesis α5β1, α6β4, αvβ3 or αvβ5). Furthermore, mass spectrometry and partial N-terminal sequencing of this peptide revealed, it is close to Lebein-1, a known anti-β1 disintegrin from Macrovipera lebetina venom. Therefore, our results show that if Dabmaurin-1 exhibits in vitro apparent anti-angiogenic effects at concentrations lower than 30 nM, it is likely because it acts as an anti-tumour disintegrin.
Keywords: angiogenesis; anti–angiogenic peptide; anti–tumour; cell adhesion molecules; disintegrin; endothelial cells; integrin; snake venom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures




References
-
- Oukkache N., Eljaoudi R., Larreche S., Chakir S., Fouad C., Hmyene A., Mion G. Snake bites in morocco: Progress and challenges. Adv. Toxicol. Toxic Effects. 2019;3:9–14. doi: 10.17352/atte.000004. - DOI
-
- Chakir S., Daoudi K., Darkaoui B., Lafnoune A., Hmyene A., Oukkache N. Research article screening of active biomolecules from the venom of the moroccan viper Daboia mauritanica. EC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019;7:144–149.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

