Exposure of CuO Nanoparticles Contributes to Cellular Apoptosis, Redox Stress, and Alzheimer's Aβ Amyloidosis
- PMID: 32033400
- PMCID: PMC7038189
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17031005
Exposure of CuO Nanoparticles Contributes to Cellular Apoptosis, Redox Stress, and Alzheimer's Aβ Amyloidosis
Abstract
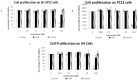
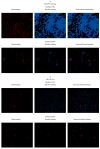
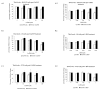
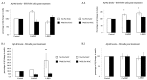
Fe2O3, CuO and ZnO nanoparticles (NP) have found various industrial and biomedical applications. However, there are growing concerns among the general public and regulators about their potential environmental and health impacts as their physio-chemical interaction with biological systems and toxic responses of the latter are complex and not well understood. Herein we first reported that human SH-SY5Y and H4 cells and rat PC12 cell lines displayed concentration-dependent neurotoxic responses to insults of CuO nanoparticles (CuONP), but not to Fe2O3 nanoparticles (Fe2O3NP) or ZnO nanoparticles (ZnONP). This study provides evidence that CuONP induces neuronal cell apoptosis, discerns a likely p53-dependent apoptosis pathway and builds out the relationship between nanoparticles and Alzheimer's disease (AD) through the involvement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and increased Aβ levels in SH-SY5Y and H4 cells. Our results implicate that exposure to CuONP may be an environmental risk factor for AD. For public health concerns, regulation for environmental or occupational exposure of CuONP are thus warranted given AD has already become a pandemic.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ; apoptosis; engineered nanomaterials; nanoparticles; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- ASTM E2456-06, Standard Terminology Relating to Nanotechnology. [(accessed on 23 January 2020)]; Available online: https://statnano.com/standard/astm/1121.
-
- Quintana A., Raczka E., Piehler L., Lee I., Myc A., Majoros I., Patri A.K., Thomas T., Mule J., Baker J.R., Jr. Design and function of a dendrimer-based therapeutic nanodevice targeted to tumor cells through thefolate receptor. Pharm. Res. 2002;19:1310–1316. doi: 10.1023/A:1020398624602. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Morawski A.M., Winter P.M., Crowder K.C., Caruthers S.D., Fuhrhop R.W., Scott M.J., Robertson J.D., Abendschein D.R., Lanza G.M., Wickline S.A. Targeted nanoparticles for quantitative imaging of sparse molecular epitopes with MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2004;51:480–486. doi: 10.1002/mrm.20010. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

