4D imaging of lithium-batteries using correlative neutron and X-ray tomography with a virtual unrolling technique
- PMID: 32034126
- PMCID: PMC7005889
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-13943-3
4D imaging of lithium-batteries using correlative neutron and X-ray tomography with a virtual unrolling technique
Abstract
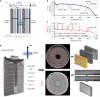
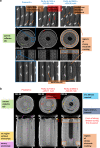
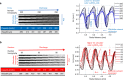
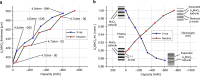
The temporally and spatially resolved tracking of lithium intercalation and electrode degradation processes are crucial for detecting and understanding performance losses during the operation of lithium-batteries. Here, high-throughput X-ray computed tomography has enabled the identification of mechanical degradation processes in a commercial Li/MnO2 primary battery and the indirect tracking of lithium diffusion; furthermore, complementary neutron computed tomography has identified the direct lithium diffusion process and the electrode wetting by the electrolyte. Virtual electrode unrolling techniques provide a deeper view inside the electrode layers and are used to detect minor fluctuations which are difficult to observe using conventional three dimensional rendering tools. Moreover, the 'unrolling' provides a platform for correlating multi-modal image data which is expected to find wider application in battery science and engineering to study diverse effects e.g. electrode degradation or lithium diffusion blocking during battery cycling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Shearing PR, Howard LE, Jørgensen PS, Brandon NP, Harris SJ. Characterization of the 3-dimensional microstructure of a graphite negative electrode from a Li-ion battery. Electrochem. commun. 2010;12:374–377. doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2009.12.038. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

