Potential Role of Integrin α₅β₁/Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) and Actin Cytoskeleton in the Mechanotransduction and Response of Human Gingival Fibroblasts Cultured on a 3-Dimension Lactide-Co-Glycolide (3D PLGA) Scaffold
- PMID: 32034900
- PMCID: PMC7027369
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.921626
Potential Role of Integrin α₅β₁/Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) and Actin Cytoskeleton in the Mechanotransduction and Response of Human Gingival Fibroblasts Cultured on a 3-Dimension Lactide-Co-Glycolide (3D PLGA) Scaffold
Abstract
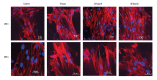
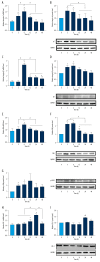
BACKGROUND The stability of orthodontic treatment is thought to be significantly affected by the compression and retraction of gingival tissues, but the underlying molecular mechanism is not fully elucidated. The objectives of our study were to explore the effects of mechanical force on the ECM-integrin-cytoskeleton linkage response in human gingival fibroblasts (HGFs) cultured on 3-dimension (3D) lactide-co-glycolide (PLGA) biological scaffold and to further study the mechanotransduction pathways that could be involved. MATERIAL AND METHODS A compressive force of 25 g/m² was applied to the HGFs-PLGA 3D co-cultured model. Rhodamine-phalloidin staining was used to evaluate the filamentous actin (F-actin) cytoskeleton. The expression level of type I collagen (COL-1) and the activation of the integrin alpha₅ß₁/focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling pathway were determined by using real-time PCR and Western blotting analysis. The impacts of the applied force on the expression levels of FAK, phosphorylated focal adhesion kinase (p-FAK), and COL-1 were also measured in cells treated with integrin alpha₅ß₁ inhibitor (Ac-PHSCN-NH 2, ATN-161). RESULTS Mechanical force increased the expression of integrin alpha₅ß₁, FAK (p-FAK), and COL-1 in HGFs, and induced the formation of stress fibers. Blocking integrin alpha₅ß₁ reduced the expression of FAK (p-FAK), while the expression of COL-1 was not fully inhibited. CONCLUSIONS The integrin alpha₅ß₁/FAK signaling pathway and actin cytoskeleton appear to be involved in the mechanotransduction of HGFs. There could be other mechanisms involved in the promotion effect of mechanical force on collagen synthesis in addition to the integrin alpha₅ß₁ pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Calreticulin silencing inhibits extracellular matrix synthesis of human gingival fibroblasts cultured on three-dimensional poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffolds by inhibiting the calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T cells 3 signalling pathway.Ann Anat. 2022 Jan;239:151820. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2021.151820. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Ann Anat. 2022. PMID: 34411706
-
Mechanical force promotes the proliferation and extracellular matrix synthesis of human gingival fibroblasts cultured on 3D PLGA scaffolds via TGF‑β expression.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Mar;19(3):2107-2114. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9882. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30664222 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing a gingival fibroblast phenotype in a perfused degradable polyurethane scaffold: mediation by TGF-β1, FGF-2, β1-integrin, and focal adhesion kinase.Biomaterials. 2014 Dec;35(38):10025-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.09.001. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Biomaterials. 2014. PMID: 25282621
-
Novel imaging methods and force probes for molecular mechanobiology of cytoskeleton and adhesion.Trends Cell Biol. 2023 Mar;33(3):204-220. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2022.07.008. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Trends Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36055943 Review.
-
LIM proteins in actin cytoskeleton mechanoresponse.Trends Cell Biol. 2014 Oct;24(10):575-83. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2014.04.009. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Trends Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24933506 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role and mechanism of compressive stress in tumor.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 16;14:1459313. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1459313. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39351360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Open Cell Form of 3D-Printed Titanium Improves Osteconductive Properties and Adhesion Behavior of Dental Pulp Stem Cells.Materials (Basel). 2021 Sep 15;14(18):5308. doi: 10.3390/ma14185308. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34576532 Free PMC article.
-
Bi-phasic effect of gelatin in myogenesis and skeletal muscle regeneration.Dis Model Mech. 2021 Dec 1;14(12):dmm049290. doi: 10.1242/dmm.049290. Epub 2021 Dec 24. Dis Model Mech. 2021. PMID: 34821368 Free PMC article.
-
Contact Angle and Cell Adhesion of Micro/Nano-Structured Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Membranes for Dental Regenerative Therapy.Dent J (Basel). 2021 Oct 20;9(11):124. doi: 10.3390/dj9110124. Dent J (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34821588 Free PMC article.
-
FAK Shutdown: Consequences on Epithelial Morphogenesis and Biomarker Expression Involving an Innovative Biomaterial for Tissue Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 10;22(18):9774. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189774. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34575938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Redlich M, Shoshan S, Palmon A. Gingival response to orthodontic force. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1999;116:152–58. - PubMed
-
- Kong S, Aoki A, Iwasaki K. Biological effects of laser irradiation on the proliferation of primary human gingival fibroblasts. J Biophotonics. 2018;11:e201700157. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

