Intracellular signaling dynamics and their role in coordinating tissue repair
- PMID: 32035001
- PMCID: PMC7187325
- DOI: 10.1002/wsbm.1479
Intracellular signaling dynamics and their role in coordinating tissue repair
Abstract
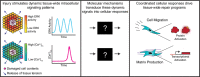
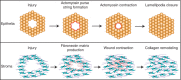
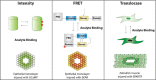
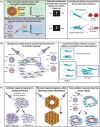
Tissue repair is a complex process that requires effective communication and coordination between cells across multiple tissues and organ systems. Two of the initial intracellular signals that encode injury signals and initiate tissue repair responses are calcium and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). However, calcium and ERK signaling control a variety of cellular behaviors important for injury repair including cellular motility, contractility, and proliferation, as well as the activity of several different transcription factors, making it challenging to relate specific injury signals to their respective repair programs. This knowledge gap ultimately hinders the development of new wound healing therapies that could take advantage of native cellular signaling programs to more effectively repair tissue damage. The objective of this review is to highlight the roles of calcium and ERK signaling dynamics as mechanisms that link specific injury signals to specific cellular repair programs during epithelial and stromal injury repair. We detail how the signaling networks controlling calcium and ERK can now also be dissected using classical signal processing techniques with the advent of new biosensors and optogenetic signal controllers. Finally, we advocate the importance of recognizing calcium and ERK dynamics as key links between injury detection and injury repair programs that both organize and execute a coordinated tissue repair response between cells across different tissues and organs. This article is categorized under: Models of Systems Properties and Processes > Mechanistic Models Biological Mechanisms > Cell Signaling Laboratory Methods and Technologies > Imaging Models of Systems Properties and Processes > Organ, Tissue, and Physiological Models.
Keywords: ERK signaling; calcium signaling; molecular mechanisms; signaling dynamics; tissue repair.
© 2020 The Authors. WIREs Systems Biology and Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

References
-
- Amano, M. , Ito, M. , Kimura, K. , Fukata, Y. , Chihara, K. , Nakano, T. , … Kaibuchi, K. (1996). Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by rho‐associated kinase (rho‐kinase). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271(34), 20246–20249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

