Identification and characterization of self-association domains on small ankyrin 1 isoforms
- PMID: 32035138
- PMCID: PMC11042479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.02.001
Identification and characterization of self-association domains on small ankyrin 1 isoforms
Abstract
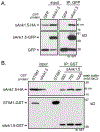
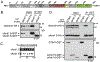
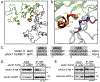
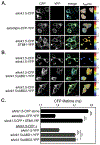
In striated muscles, the large scaffolding protein obscurin and a small SR-integral membrane protein sAnk1.5 control the retention of longitudinal SR across the sarcomere. How a complex of these proteins facilitates localization of longitudinal SR has yet to be resolved, but we hypothesize that obscurin interacts with a complex of sAnk1.5 proteins. To begin to address this hypothesis, we demonstrate that sAnk1.5 interacts with itself and identify two domains mediating self-association. Specifically, we show by co-precipitation and FLIM-FRET analysis that sAnk1.5 and another small AnkR isoform (sAnk1.6) interact with themselves and each other. We demonstrate that obscurin interacts with a complex of sAnk1.5 proteins and that this complex formation is enhanced by obscurin-binding. Using FLIM-FRET analysis, we show that obscurin interacts with sAnk1.5 alone and with sAnk1.6 in the presence of sAnk1.5. We find that sAnk1.5 self-association is disrupted by mutagenesis of residues Arg64-Arg69, residues previously associated with obscurin-binding. Molecular modeling of two interacting sAnk1.5 monomers facilitated the identification of Gly31-Val36 as an additional site of interaction, which was subsequently corroborated by co-precipitation and FLIM-FRET analysis. In closing, these results support a model in which sAnk1.5 forms large oligomers that interact with obscurin to facilitate the retention of longitudinal SR throughout skeletal and cardiac myocytes.
Keywords: Ankyrin; Obscurin; Sarcoplasmic reticulum; Self-association; sAnk1.5.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Borisov AB, Sutter SB, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A, Bloch RJ, Westfall MV, Russell MW, Essential role of obscurin in cardiac myofibrillogenesis and hypertrophic response: evidence from small interfering RNA-mediated gene silencing, Histochem. Cell Biol 125 (2006) 227–238. - PubMed
-
- Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A, Catino DH, Strong JC, Sutter S, Borisov AB, Pumplin DW, Russell MW, Bloch RJ, Obscurin modulates the assembly and organization of sarcomeres and the sarcoplasmic reticulum, FASEB J. 20 (2006) 2102–2111. - PubMed
-
- Raeker MO, Su F, Geisler SB, Borisov AB, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A, Lyons SE, Russell MW, Obscurin is required for the lateral alignment of striated myofibrils in zebrafish, Dev. Dyn 235 (2006) 2018–2029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

