Advances in elucidating the function of leucine-rich repeat protein kinase-2 in normal cells and Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 32036294
- PMCID: PMC7262585
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2020.01.001
Advances in elucidating the function of leucine-rich repeat protein kinase-2 in normal cells and Parkinson's disease
Abstract
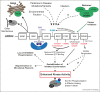
Autosomal dominant missense mutations that hyperactivate the leucine-rich repeat protein kinase-2 (LRRK2) are a common cause of inherited Parkinson's disease and therapeutic efficacy of LRRK2 inhibitors is being tested in clinical trials. In this review, we discuss the nuts and bolts of our current understanding of how the LRRK2 is misregulated by mutations and how pathway activity is affected by LRRK2 binding to membrane, microtubule filaments, and 14-3-3, as well as by upstream components such as Rab29 and VPS35. We discuss recent work that points toward a subset of Rab proteins comprising key physiological substrates that bind new sets of effectors, such as RILPL1/2, JIP3 and JIP4 after phosphorylation by LRRK2. We explore what is known about how LRRK2 regulates ciliogenesis, the endosomal-lysosomal system, immune responses and interplay with alpha-synuclein and tau and how this might be linked to Parkinson's' disease.
Keywords: Ciliogenesis; Lysosomal stress; Neuroinflammation; Protein kinase; RILPL1; Rab GTPase; Signal transduction.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest statement Nothing declared.
Figures


References
-
- Nukada H., Kowa H., Saitoh T., Tazaki Y., Miura S. [A big family of paralysis agitans (author's transl)] Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1978;18:627–634. - PubMed
-
- Funayama M., Hasegawa K., Kowa H., Saito M., Tsuji S., Obata F. A new locus for Parkinson's disease (PARK8) maps to chromosome 12p11.2-q13.1. Ann Neurol. 2002;51:296–301. - PubMed
-
- Zimprich A., Biskup S., Leitner P., Lichtner P., Farrer M., Lincoln S., Kachergus J., Hulihan M., Uitti R.J., Calne D.B. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron. 2004;44:601–607. - PubMed
-
- Paisan-Ruiz C., Jain S., Evans E.W., Gilks W.P., Simon J., van der Brug M., Lopez de Munain A., Aparicio S., Gil A.M., Khan N. Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson's disease. Neuron. 2004;44:595–600. - PubMed
-
- Funayama M., Hasegawa K., Ohta E., Kawashima N., Komiyama M., Kowa H., Tsuji S., Obata F. An LRRK2 mutation as a cause for the parkinsonism in the original PARK8 family. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:918–921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

